Which Middle Eastern Nation Has More Military Personnel Than Israel and Saudi Arabia Combined?
Is World War III on the horizon? While nobody wants to imagine that we’re entering into another world war, this question has been on the minds of citizens across the globe, especially in the face of increasing tensions between global powers. Syria has been negotiating with Russia and Turkey regarding military presence in the country, […] The post Which Middle Eastern Nation Has More Military Personnel Than Israel and Saudi Arabia Combined? appeared first on 24/7 Wall St..

Is World War III on the horizon? While nobody wants to imagine that we’re entering into another world war, this question has been on the minds of citizens across the globe, especially in the face of increasing tensions between global powers. Syria has been negotiating with Russia and Turkey regarding military presence in the country, but at the same time is attempting to improve its relationship with the United States. The U.S. has also increased its own presence in the Middle East, with Haaretz reporting that this is “the largest offensive deployment to the Middle East since the Israel-Hamas war began in October 2023.” This comes on the tail of ongoing U.S. conflict between Houthi rebels in Yemen, who have attacked American troops and ships, as well as President Donald Trump’s growing frustration with Iran’s nuclear program — Iran has recently been strengthening nuclear sites. With no signs that these tensions will slow down or be solved, many countries are bolstering their military forces in preparation. (These are America’s best friends in the Arab world.)
If war were to break out, military forces, as well as military aircraft and vehicles, would play a significant part in which countries emerge victorious. Using Military Firepower’s 2025 Military Strength Ranking, an annual ranking that assesses 145 countries’ military power based on over 60 different factors, 24/7 Wall St. broke down the 15 Middle Eastern militaries with the most military personnel. We listed these countries in order from least to most military personnel. Additional information, including military vehicle and aircraft counts, population, fit-for-service population, and a breakdown of personnel also came from Military Firepower. We also included each country’s military strength ranking; the closer to 0.000, the more powerful the military overall.
This previously published article was updated on April 24, 2025 to provide new Military Strength Ranking data and to provide sources on the current conflicts emerging in the Middle East that may soon hit a breaking point.
Why Are We Covering This Now?
The military dynamics in the Middle East are complicated, to say the least. The region’s historical and ongoing political tensions have shaped, and continue to shape, regional progress and development. Territorial disputes are one reason why the Middle East is so fraught with conflict, but that’s not the sole reason; resources, religious divides, and alternate belief systems also play a role. For investors, understanding the military forces in the Middle East, especially in strategic areas like Israel or Saudi Arabia, gives you a better idea of how global security and energy markets might change.
But learning about Middle Eastern military powers also provides insight into how the United States might fare should another war with the Middle East break out. And this potential is closer than you think — U.S. President Donald Trump recently told Congress that he had directed the Department of Defense to deploy additional troops to the Middle East to strike against Yemeni Houthi militants who have had deleterious effects on American shipping.
Here are the 15 Middle Eastern countries with the most powerful militaries:
15. Qatar

- Total military personnel: 87,050
- Active personnel: 66,550
- Reserves: 15,000
- Paramilitary forces: 5,500
- Total population: 2,552,088
- Fit-for-service: 490,001
- Total military aircraft: 251
- Total military vehicles: 5,024 (including 99 tanks, 58 artillery units, and 16 MLRS units)
- Military strength score and world rank: 1.4307 – #72 out of 145
Qatar’s military history is largely shaped by its strategic position on the Arabian Peninsula, and its substantial natural gas and oil reserves. Since its independence from Britain in 1971, Qatar has rapidly modernized its military. This modernization has only ramped up as the country has gained much more economic power from the oil and gas trade. Qatar has procured advanced military technology from the U.S., France, and other nations, including state-of-the-art aircraft like F-15 and Rafale jets. Qatar has also been developing its naval force to protect its extensive coastline, as well as its oil and gas interests, and currently has a total of 115 naval vessels.
14. Kuwait

- Total military personnel: 103,500
- Active personnel: 72,000
- Reserves: 24,000
- Paramilitary forces: 7,500
- Total population: 3,138,355
- Fit-for-service: 1,449,920
- Total military aircraft: 128
- Total military vehicles: 5,636 (including 367 tanks, 74 artillery units, and 27 MLRS units)
- Military strength score and world rank: 1.6982 – #79 out of 145
Kuwait’s location at the northern edge of the Persian Gulf has heavily influenced its military history over the years. The country was in the dominion of the Ottoman Empire before becoming a British protectorate in the early 20th century. Kuwait gained independence in 1961. Kuwait was later invaded by Iraq in 1990, which precipitated the Gulf War. Saddam Hussein’s push into Kuwait was largely driven by disputes over oil and debt. The international response from this served to liberate Kuwait, but Saddam was not removed from power for more than a decade.
13. Bahrain

- Total military personnel: 129,900
- Active personnel: 18,400
- Reserves: 110,000
- Paramilitary forces: 1,500
- Total population: 1,566,888
- Fit-for-service: 720,768
- Total military aircraft: 132
- Total military vehicles: 2,764 (including 150 tanks, 64 artillery units, and 17 MLRS units)
- Military strength score and world rank: 1.7448 – #81 out of 145
Although Bahrain has a much less tumultuous military history than its neighbors, the country occupies a strategic position in the Persian Gulf. This island nation was occupied by the Portuguese in the 16th century but later fell under Persian and then Ottoman control. In the 19th century, Bahrain was a British protectorate, which significantly bolstered its military and foreign policy. However, the country gained independence in 1971 and establish its own military and national defense forces. Bahrain has maintained ties with Western powers which have improved its military capabilities over the years, especially its naval power. Currently, Bahrain has 64 naval vessels.
12. Oman
- Total military personnel: 152,600
- Active personnel: 42,600
- Reserves: 100,000
- Paramilitary forces: 10,000
- Total population: 3,901,992
- Fit-for-service: 1,291,559
- Total military aircraft: 128
- Total military vehicles: 4,084 (including 150 tanks and 164 artillery units)
- Military strength score and world rank: 1.8047 – #82 out of 145
Oman was a powerful empire in the 17th and 18th centuries, with colonies around the Indian Ocean and enough naval strength to back it up. This allowed the country to resist Portuguese and Persian forces. In the 19th century, Oman saw a drastic leap in its military capabilities following an alliance with the British Empire. Ultimately, this alliance helped Oman modernize its forces and keep pace with the West. In more recent years, Oman has remained neutral in regional conflicts, instead focusing on its national defense and maintaining a fairly modern force.
11. Lebanon

- Total military personnel: 160,000
- Active personnel: 60,000
- Reserves: 35,000
- Paramilitary forces: 65,000
- Total population: 5,364,482
- Fit-for-service: 1,775,644
- Total military aircraft: 80
- Total military vehicles: 4,538 (including 116 tanks, 365 artillery units, and 11 MLRS units)
- Military strength score and world rank: 2.5981 – #115 out of 145
Located on the Mediterranean, Lebanon’s military history centers around many regional conflicts. The country gained independence from the French in 1943. But with such an ethnically and religiously diverse population, Lebanon has faced challenges since. The Lebanese Civil War, starting in 1975, saw multiple factions attempting to gain control and then foreign powers intervening as well. In the post-civil war years, Lebanon’s military has focused on rebuilding and modernization with considerable assistance from international powers. Despite its smaller size, Lebanon’s military plays an important role in maintaining internal stability as it contends with issues from non-state actors like Hezbollah and border tensions with Israel.
10. Jordan

- Total military personnel: 200,500
- Active personnel: 100,500
- Reserves: 65,000
- Paramilitary forces: 35,000
- Total population: 11,174,024
- Fit-for-service: 2,983,464
- Total military aircraft: 274
- Total military vehicles: 16,624 (including 1,458 tanks, 438 artillery units, and 56 MLRS units)
- Military strength score and world rank: 1.6139 – #75 out of 145
Jordan has a rich military history in a region that has been embroiled by conflict for decades. The Hashemite Kingdom of Jordan was established after World War I from the breaking of the Ottoman Empire. It would gain its full independence from Britain in 1946. Within the last century, Jordan’s main military engagements have included conflicts with Israel, notably during the 1948 Arab-Israeli War and again in 1967 during the Six-Day War, where Jordan lost control of the West Bank. These conflicts ultimately shaped Jordan’s borders and its military strategies going forward. Currently, Jordan maintains ties to Western powers that help with its military modernization efforts. Also, the country acts as a stabilizing power within the region, typically acting as a mediator in peace talks. It has also maintained a peace treaty with Israel since 1994.
9. United Arab Emirates

- Total military personnel: 207,000
- Active personnel: 65,000
- Reserves: 130,000
- Paramilitary forces: 12,000
- Total population: 10,032,213
- Fit-for-service: 4,945,881
- Total military aircraft: 551
- Total military vehicles: 8,707 (including 354 tanks, 264 artillery units, and 49 MLRS units)
- Military strength score and world rank: 1.0186 – #54 out of 145
The United Arab Emirates has a relatively brief but really dynamic military history. The country was formed in 1971 when seven emirates combined forces to build a nation with a strong military geared towards advanced technology and modernization. The U.S. and France are the main sellers of this tech to the UAE, and in turn, the UAE has been involved in regional operations in the Gulf War, Yemen, and against ISIS. The UAE’s power extends further beyond its relatively small territory in the Persian Gulf. In fact, the country has been projecting power abroad where it has established military bases in the Horn of Africa and beyond.
8. Syria

- Total military personnel: 270,000
- Active personnel: 170,000
- Reserves: 50,000
- Paramilitary forces: 50,000
- Total population: 23,865,423
- Fit-for-service: 13,245,310
- Total military aircraft: 207
- Total military vehicles: 11,148 (including 365 tanks, 731 artillery units, and 204 MLRS units)
- Military strength score and world rank: 1.2771 – #64 out of 145
One of the reasons why Syria has been so embroiled in military conflict throughout history is its strategic location, which has made it a point of contention both regionally and internationally. Historically, Syria has been part of major empires due to its position between the Mediterranean and the Arab world. The country gained independence from France in 1946, and has since been involved in several wars with Israel and the Lebanese Civil War. The most recent chapter in Syria’s military history began in 2011 with the Syrian Civil War, which was brought on by Arab Spring protests. This was hotly contested by multiple factions including ISI, Kurdish forces, as well as foreign military powers like Russia and the U.S., Turkey and others. Recent moves have brought into question what the future of the country will look like.
7. Iraq

- Total military personnel: 293,000
- Active personnel: 193,000
- Reserves: 0
- Paramilitary forces: 100,000
- Total population: 42,083,436
- Fit-for-service: 14,308,368
- Total military aircraft: 391
- Total military vehicles: 37,288 (including 1,025 tanks, 1,044 artillery units, and 572 MLRS units)
- Military strength score and world rank: 0.7738 – #43 out of 145
Officially gaining independence in 1932 from the British, Iraq was still subject to Britain’s influence until the late 1950s. The country saw Saddam Hussein rise to power in 1979 with the Ba’ath Party. Hussein rapidly expanded the military during his time, even waging a war with Iran from 1980 to 1988. Saddam would later invade Kuwait in 1990, leading to the Gulf War. However, a U.S. led invasion in 2003 would ultimately topple the dictator and create instability within the country as well as the formation of multiple insurgent factions to the new government. Currently, Iraq is in the state of rebuilding its military to deal with internal threats.
6. Saudi Arabia

- Total military personnel: 407,000
- Active personnel: 257,000
- Reserves: 0
- Paramilitary forces: 150,000
- Total population: 36,544,431
- Fit-for-service: 17,468,238
- Total military aircraft: 917
- Total military vehicles: 19,040 (including 840 tanks, 799 artillery units, and 321 MLRS units)
- Military strength score and world rank: 0.4201 – #24 out of 145
Saudi Arabia as we know it today was founded in 1932. This came decades after Abdulaziz Al Saud (Ibn Saud) unified the Saudi state after conquering Riyadh in 1902. The discovery of oil in the 1930s catapulted the Kingdom to prominence on the world stage. Through this oil trade, Saudi Arabia has profited incredibly with many of its Western trading partners like the United States. Along with the oil trade, Saudi Arabia has procured advanced weaponry and aircraft from these Western powers, making it one of the more dominant military powers in the region. Saudi Arabia would also play an important role in the Gulf War as part of the coalition that expelled Iraqi forces from Kuwait.
5. Israel

- Total military personnel: 670,000
- Active personnel: 170,000
- Reserves: 465,000
- Paramilitary forces: 35,000
- Total population: 9,402,617
- Fit-for-service: 3,281,513
- Total military aircraft: 611
- Total military vehicles: 35,985 (including 1,300 tanks, 523 artillery units, and 183 MLRS units)
- Military strength score and world rank: 0.2661 – #15 out of 145
Israel was formed in 1948 and was plunged immediately into conflict with neighboring Arab states in an attempt to prevent its establishment. Over the coming decades, and even currently, Israel would be the central locale of conflict for this region. Other notable conflicts that Israel has survived, and even in some expanded its territory, include the Suez Crisis, Six-Day War, Yom Kippur War, and other conflicts with Lebanon. Its most recent engagement with Hamas has devastated the Gaza Strip, and the international community is concerned with the ongoing situation to say the least. Today, Israel has compulsory military service for its citizens, who must serve in the Israeli Defense Forces (IDF).
4. Turkiye

- Total military personnel: 883,900
- Active personnel: 355,200
- Reserves: 378,700
- Paramilitary forces: 150,000
- Total population: 84,119,531
- Fit-for-service: 36,087,279
- Total military aircraft: 1,083
- Total military vehicles: 61,173 (including 2,238 tanks, 2,745 artillery units, and 296 MLRS units)
- Military strength score and world rank: 0.1902 – #9 out of 145
Turkey’s military history is deeply rooted in its role as the seat of power during the Ottoman Empire. Also, its strategic location, bridging Europe and Asia, is central to its military history and the composition of its forces as well. In part, Turkey largely owes its NATO membership to this fact. The dissolution of the Ottoman Empire in the wake of World War I and the subsequent Turkish War of Independence were important events that not only established the boundaries of the new nation but also created a strong military tradition that continues to influence Turkey today.
3. Iran

- Total military personnel: 1,180,000
- Active personnel: 610,000
- Reserves: 350,000
- Paramilitary forces: 220,000
- Total population: 88,386,937
- Fit-for-service: 41,541,860
- Total military aircraft: 551
- Total military vehicles: 65,825 (including 1,713 tanks, 2,462 artillery units, and 1,517 MLRS units)
- Military strength score and world rank: 0.3048 – #16 out of 145
Iran can trace its military history back to the days of the Persian Empire. But today, many Western powers currently consider Iran an antagonist in the region which have led to sanctions against the country, hampering military modernization. Despite efforts by Western powers to contain Iran, the country still has a formidable military force with nuclear aspirations. Recently, Pennsylvania Senator John Fetterman stated that the U.S. should “waste that sh**,” referring to Iran’s nuclear facilities.
2. Egypt

- Total military personnel: 1,220,000
- Active personnel: 440,000
- Reserves: 480,000
- Paramilitary forces: 300,000
- Total population: 111,247,248
- Fit-for-service: 38,269,053
- Total military aircraft: 1,093
- Total military vehicles: 41,012 (including 3,620 tanks, 2,018 artillery units, and 528 MLRS units)
- Military strength score and world rank: 0.3427 – #19 out of 145
Straddling the Middle East and Africa, Egypt is in control of one of the most important shipping lanes in the world, the Suez Canal, which it nationalized in 1956. This crossroads has historically helped Egypt rise to prominence as a military power. From the days of the Pharaohs millennia ago to now, Egypt has been a perennial military powerhouse. Just over a decade ago, the Egyptian military played a significant role in the Arab Spring, particularly in the ousting of President Hosni Mubarak in 2011 and President Mohamed Morsi in 2013.
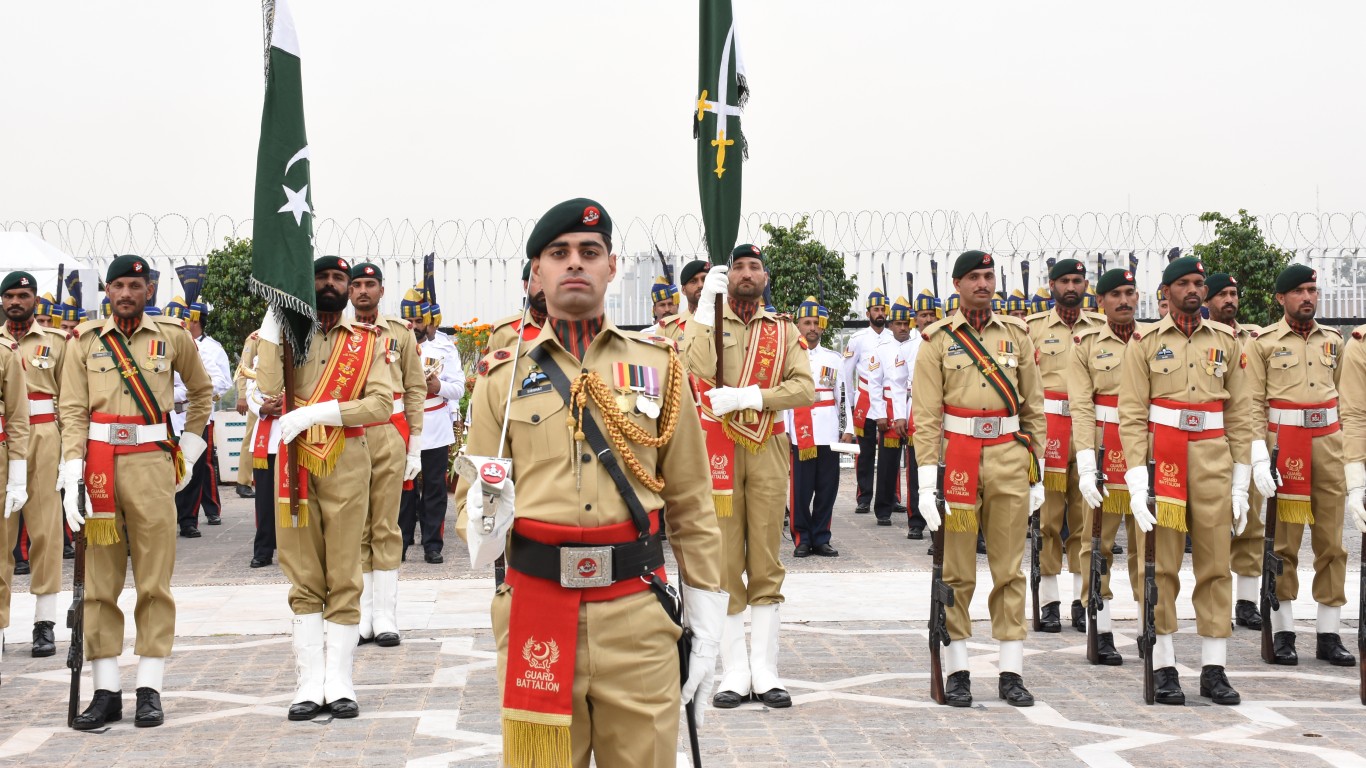
1. Pakistan

- Total military personnel: 1,704,000
- Active personnel: 654,000
- Reserves: 550,000
- Paramilitary forces: 500,000
- Total population: 252,363,571
- Fit-for-service: 85,803,614
- Total military aircraft: 1,399
- Total military vehicles: 17,516 (including 2,627 tanks, 3,291 artillery units, and 600 MLRS units)
- Military strength score and world rank: 0.2513 – #12 out of 145
Pakistan’s military history is deeply tied with its formation in 1947, when it separated from India. This division would set the stage for India and Pakistan to slug it out in the decades to come. The first Indo-Pakistani War was waged over Kashmir which each nation claimed as their own. There would be subsequent wars in 1965 and 1971. The conflict in 1971 was a severe loss for Pakistan and ultimately culminated in the creation of Bangladesh. Pakistan has also participated in other regional conflicts like the Soviet-Afghan War, where it supported Afghan mujahideen groups with the aid of the U.S. and Saudi Arabia. The Pakistani military has also played a significant role in the country’s politics, having directly ruled Pakistan during various periods through military coups. Currently, its military ranks as one of the top 10 strongest in the world.
The post Which Middle Eastern Nation Has More Military Personnel Than Israel and Saudi Arabia Combined? appeared first on 24/7 Wall St..