The US Military Budget and the President Who Grew It by 39%
The United States spends more on its military than the next ten largest military budgets in the world combined, most of which are our allies. Excluding China, the United States spends more on its military than the rest of the world combined. We have the third-largest military in the world and we spend more than […] The post The US Military Budget and the President Who Grew It by 39% appeared first on 24/7 Wall St..

The United States spends more on its military than the next ten largest military budgets in the world combined, most of which are our allies. Excluding China, the United States spends more on its military than the rest of the world combined. We have the third-largest military in the world and we spend more than double the rest of NATO combined on our military. But where does this money go, and which presidents are responsible for the largest increases to our military budget?
Key Points
-
Republican presidents have historically increased the military budget drastically, while democrats decrease it.
-
Politicians like to increase the military budget beyond what is asked in order to score political points.
-
4 million Americans are set to retire this year. If you want to join them, click here now to see if you’re behind, or ahead. It only takes a minute. (Sponsor)
We compared the budget for the Department of Defense throughout its history and found the largest increases enacted by each administration. In this article, we include the three administrations that increased the military budget the most based on a total percentage increase during their term as president.
History of the U.S. Military Budget

The military budget of the United States pays for more than just guns and tanks, it also covers anything that is remotely military-related. This includes healthcare, salaries, and everything related to building and maintaining arms, weapons, and facilities in the United States and abroad. The budget is divided between the Navy, Army, Air Force, Marine Corps, Coast Guard, and Space Force.
The U.S. military budget reached a peak (as a percent of GDP) during World War II before dropping significantly after the resolution of the war. It has slowly and continuously increased ever since, surpassing the peak of the 1940s in terms of percent of GDP and in total dollars spent.
After World War II, the United States renamed the National Military Establishment as the Department of Defense in 1949 in probably one of the biggest instances of irony in the history of planet Earth. This new department set up the groundwork for the military-industrial complex we see today.
Besides the branches of the military within the Department of Defense, there are also four intelligence services that get a portion of the budget. These are the Defense Intelligence Agency, the National Geospatial-Intelligence Agency, the National Reconnaissance Office, and the National Security Agency.
Current Military Budget

By law, each federal agency must release a public audit of its finances every year, and the Department of Defense is the only agency to have never released a single audit. Yet, investigations into the finances of the department show illegal, inaccurate, and unsubstantiated changes to the financial documents to force them to match the budget in the U.S. Treasury. The Department of Defense has repeatedly suppressed and hidden third-party audits of its finances, including a 2015 audit that showed it could cut $125 billion from its budget without firing anyone. In 2022, the Department of Defense could not account for 60% of its entire budget.
The Department of Defense has the highest amount of budgetary resources allocated to it compared to all other federal agencies, and it is more than half of the total yearly spending in the U.S. federal discretionary budget (which does not include mandatory expenditures like Social Security).
The Department of Defense requested a total budget of $849.8 billion for 2025, and the U.S. Congress approved a resolution to fund it through March of 2025. This is a substantial increase over the $842 billion for 2024 and $782 billion in 2023.
Congress regularly increased the military budget beyond what the president or even the Department of Defense requested or even wanted. For example, President Biden requested a military budget of $715 billion for 2022, but the Senate Armed Services Committee instead approved a budget of $740 billion.
Also, President Obama requested $664 billion for the Department of Defense for 2009, but Congress approved a final budget of $680 billion instead.
Why does Congress do this? Americans love war, and they love to see their elected officials being aggressive when it comes to supporting the military and the armed forces. So, our representatives often ask for and support legislation and budgets that are in excess of what we need in order to score political points. It would seem that U.S. pro-military propaganda has begun to come back and bit it in the behind.
Please remember, that the budgets for each of the branches of the military that follow are according to the Department of Defense and are impossible to verify. They are also unlikely to be true.
Department of the Air Force Budget

The U.S. Air Force receives around 22% of the military budget. The largest expenses for the Air Force are, in order: military personnel (including salaries and training), operation and maintenance, weapon procurement, research and development, construction projects, family housing, and management funds.
Department of the Army Budget

The U.S. Army receives the most military funding, about 32% of the total budget for the Department of Defense. It is the largest military branch in the United States with around 1,005,725 soldiers (including the Army Reserve and National Guard) as of 2022. It has been the primary force in projecting American power and influence since World War II.
Department of the Navy Budget

The U.S. Navy receives around 23% of the total military budget (not including the Marines). It includes the U.S. Navy, the Marine Corps, and the Coast Guard. The Navy has around 400,000 military members with around 25% in reserve. The U.S. Navy is widely regarded as the most powerful navy in the world with the largest displacement as of 2021 from 299 combat vessels and 4,012 aircraft. It has the most aircraft carriers of any country (at 11, currently, and more to be launched soon).
The Marine Corps receives its budget from the Department of the Navy, which is about 4% of the total military budget.
Senator John McCain repeatedly killed legislation that was meant to rename the Navy Department as the Department of the Navy and Marine Corps. The legislation had broad support in both houses of Congress.
Other Military Budget Expenses

Around 15% of the remaining budget is expenses that are shared between the military branches and other operations and military activities. Another 4% (approximately) is for classified intelligence operations.
#3 Donald Trump (2017–2020)

- Total budget increase: 8%
On the campaign trail, Trump promised to pass a massive build-up of America’s military power, and even though he backtracked once he was in office, he still found himself in third place on our list.
After his election, President Trump withdrew the United States from the Intermediate-Range Nuclear Forces Treaty, withdrew from the Open Skies Treaty, and complained that the United States spent too much money on an uncontrollable arms race with China. He called the current military budget “crazy” yet praised his own increases in military spending.
In 2018, Trump bragged that he had made the largest budget increase ever, enacted the first military pay increase in ten years, and increased the military budget beyond 4% of GDP. All of these assertions were lies.
Trump also pardoned a number of military members who had committed war crimes. This includes when he intervened in the Navy process and pardoned Eddie Gallagher who shot and killed unarmed civilians, which angered and offended many military officers.
Trump drastically increased how often the government used drone strikes against military and civilian targets in Iraq, Afghanistan, Somalia, Yemen, and Syria. He reduced transparency in drone strike reports and reduced the accountability related to drone strikes. In 2019 he ended the policy of reporting how many civilians are killed in each U.S. drone strike. He said that reporting civilian deaths was “unnecessary”.
Why Did Trump Increase the Military So Much?
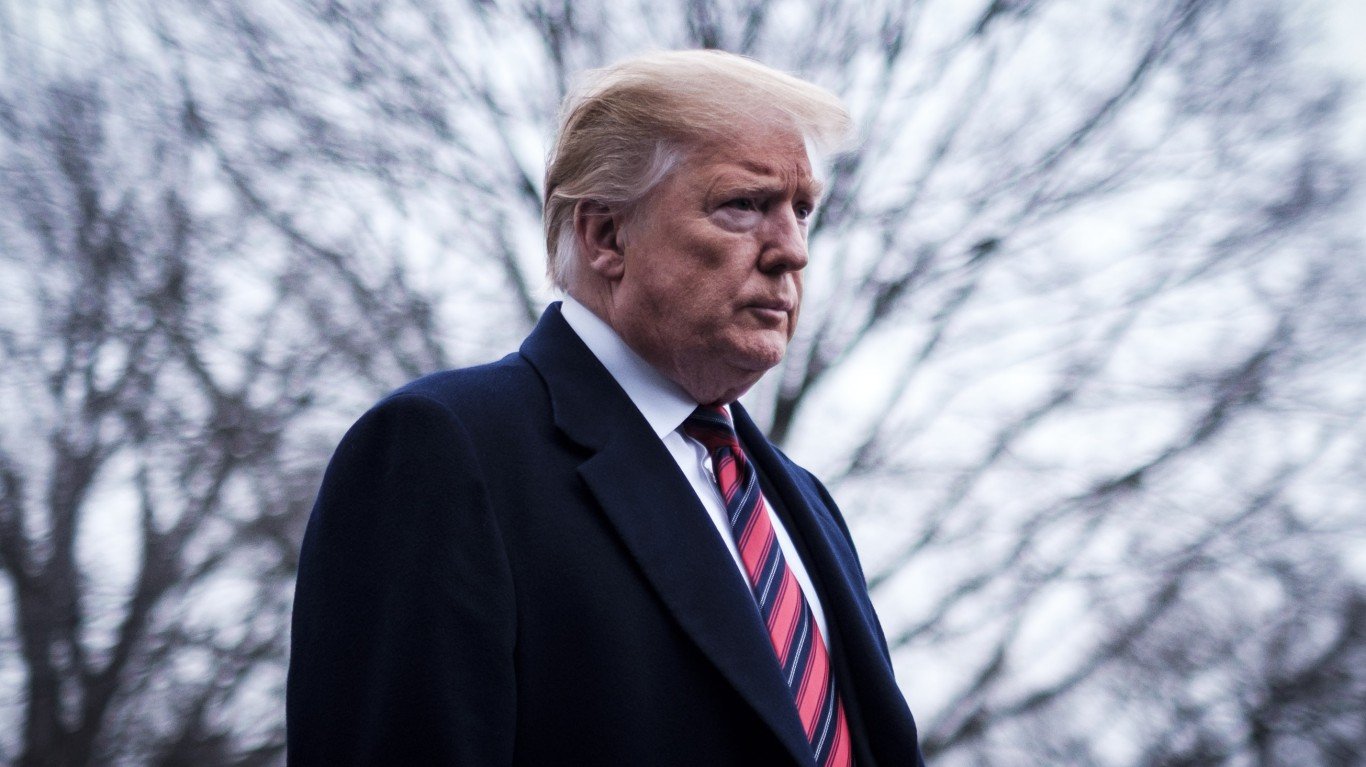

Trump repeatedly complained that he inherited “depleted” armed forces from Obama, which several high-ranking military officers disputed. Despite this, and his promises to increase funding considerably, overall military spending was lower than during Obama’s first term as president.
Trump shifted more responsibility for military engagements from the president to the Pentagon. Of this move, Mother Jones said “the US military was pursuing a strategy that tolerated a higher risk of bloodshed.”
Trump drastically decreased the number of troops in Afghanistan, reducing the amount to its lowest point since 2001. Instead, he increased the use of drones. As a result, the number of civilian deaths due to American forces skyrocketed during his presidency. Trump also signed a deal with the Taliban in 2020, promising to withdraw U.S. troops and releasing 5,000 Taliban members. These members were among the forces that overthrew the Afghan government in 2021.
Overall, the Trump presidency set itself apart from previous administrations by openly praising and admiring authoritarian rulers, rejecting key human rights, and ignoring their abuses. According to Fox News, CNN, and The Atlantic, Trump often and frequently disparaged and mocked military officers, American soldiers, and fallen soldiers with demeaning and crude language to other world leaders in public and private.
#2 Ronald Reagan

- Total budget increase: 16%
Even though the Cold War was cooling off when Reagan took office, his campaign promises and personal ideology caused him to escalate the Cold War with the USSR and drastically increase not only military spending but also offensive and violent rhetoric.
Reagan won popularity by campaigning against the social changes made during the Civil Rights era and through Affirmative Action, and by promising to return the U.S. to military supremacy.
Reagan more than doubled the military budget between 1981 and 1985. He is responsible for the first and second highest year-over-year military budget increases.
In order to help pay for his massive increases, Reagan proposed cuts to Social Security, and cut funding for food stamps, unemployment benefits, subsidized housing, and Aid to Families with Dependent Children. He also raised the retirement age and increased Social Security taxes.
Why Did Reagan Increase the Military So Much?
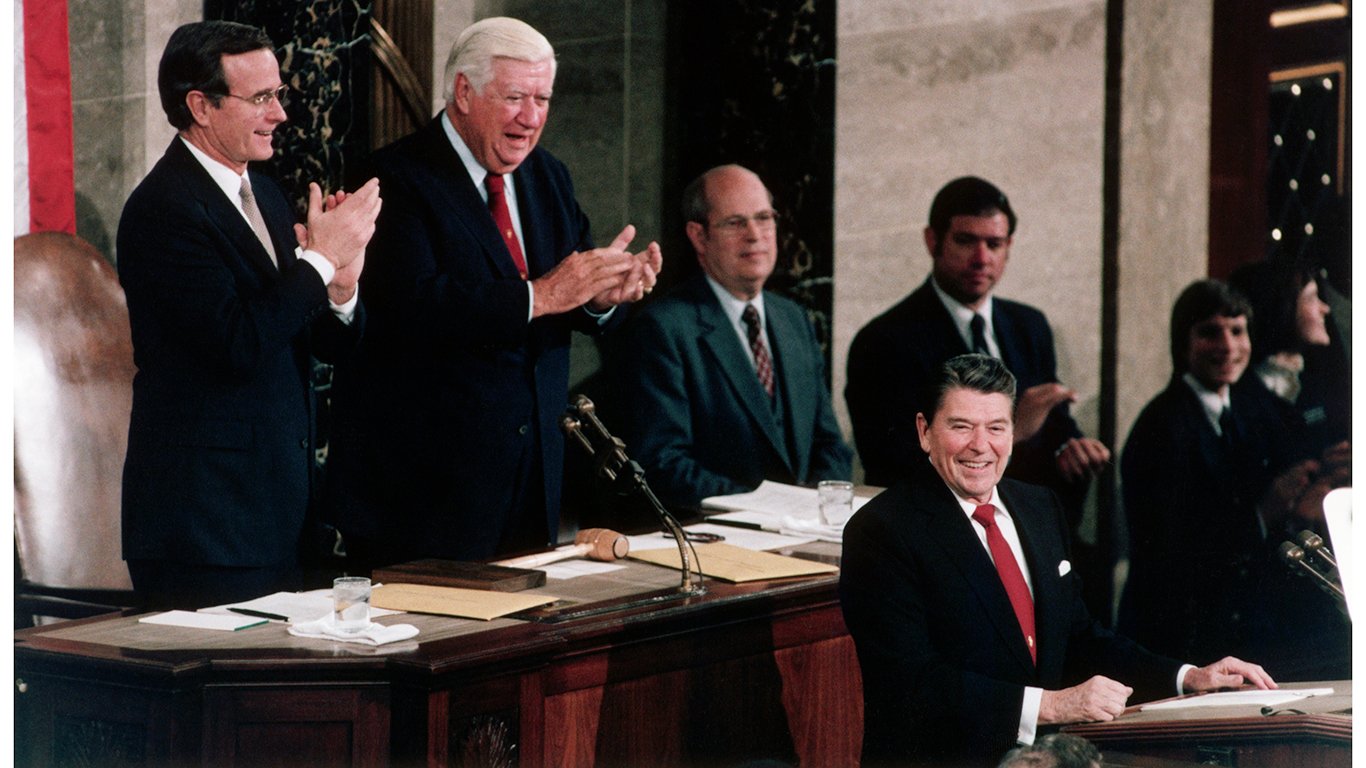

Reagan used the threat of Communism to scare millions of Americans into voting him into office. Once elected, he forgot his promises of balanced budgets and immediately ordered huge military increases.
Reagan ignored multiple opportunities to create peace with the USSR, and instead launched several new projects to protect the United States from hypothetical Soviet threats (like protecting the country from missiles launched from space) and increased the U.S. presence and engagement in foreign conflicts.
He was the first president to reject containment and de-escalation with the Soviet Union and preferred to believe that it could be outright defeated.
Reagan supplied funds, resources, and weapons to the Mujahideen in Afghanistan (which would eventually lead to the rise of Osama bin Laden), supported the fascist Guatemalan government as it committed genocide, and funded the Chad government as it committed mass killings of its own people. Reagan ordered the invasion of Grenada, armed the Contras in Nicaragua in the Iran-Contra affair, and more.
By the time Reagan left office, the military budget had been increased by 43% over its peak during the Vietnam War.
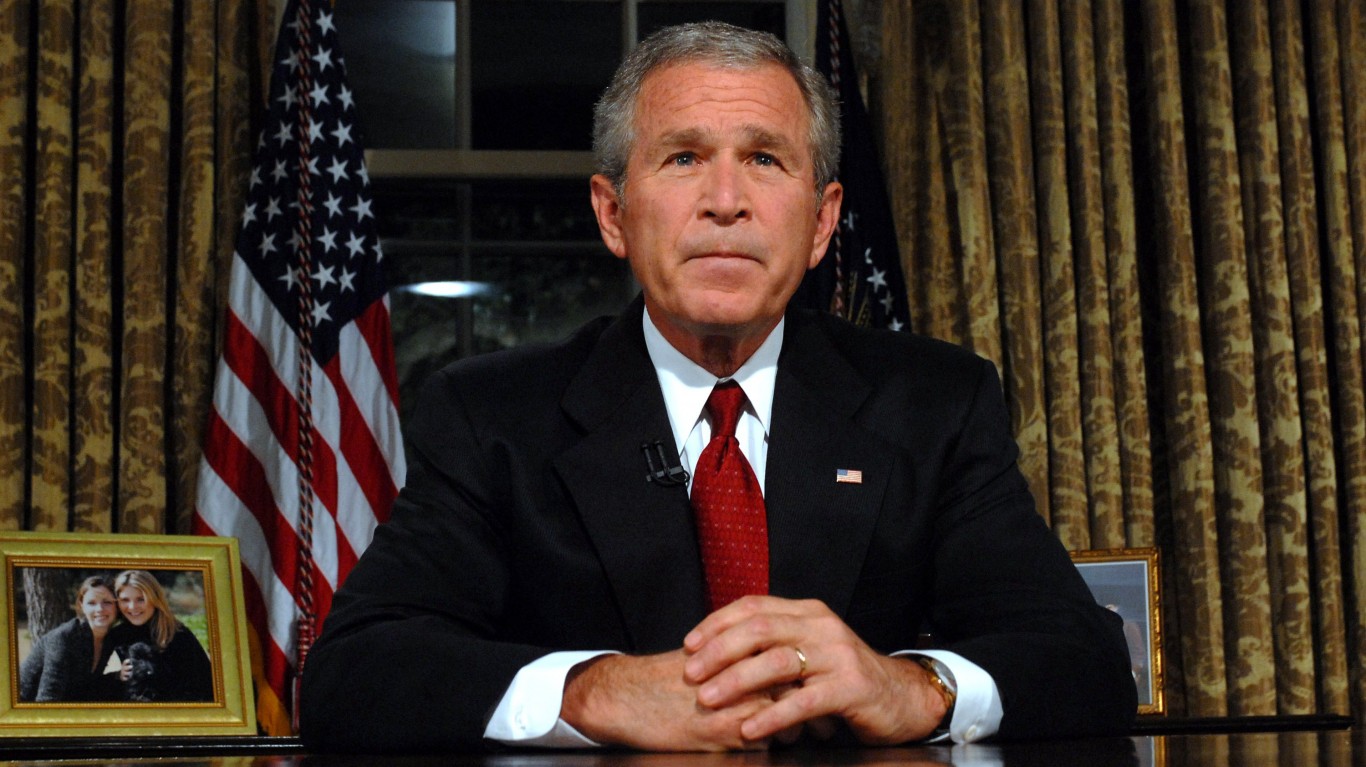
#1 George W. Bush
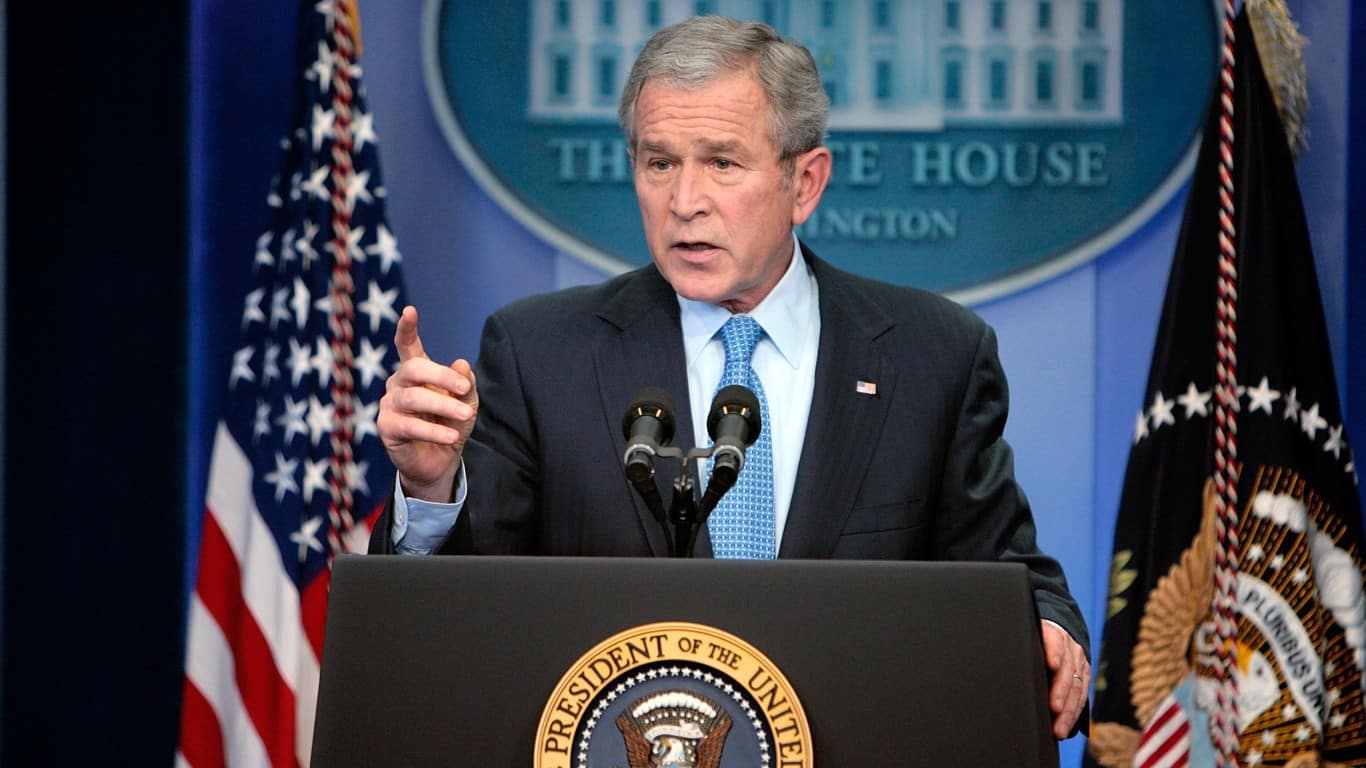

- Total budget increase: 39%
George W. Bush continued the neoliberal policies of his predecessors and laid the groundwork for today’s neoconservatism. Whether Bush had plans to expand the military and government as much as he did, we may never know, as the September 11 attacks set the tone for his entire presidency and forever changed the world.
Why Did Bush Increase the Military So Much?
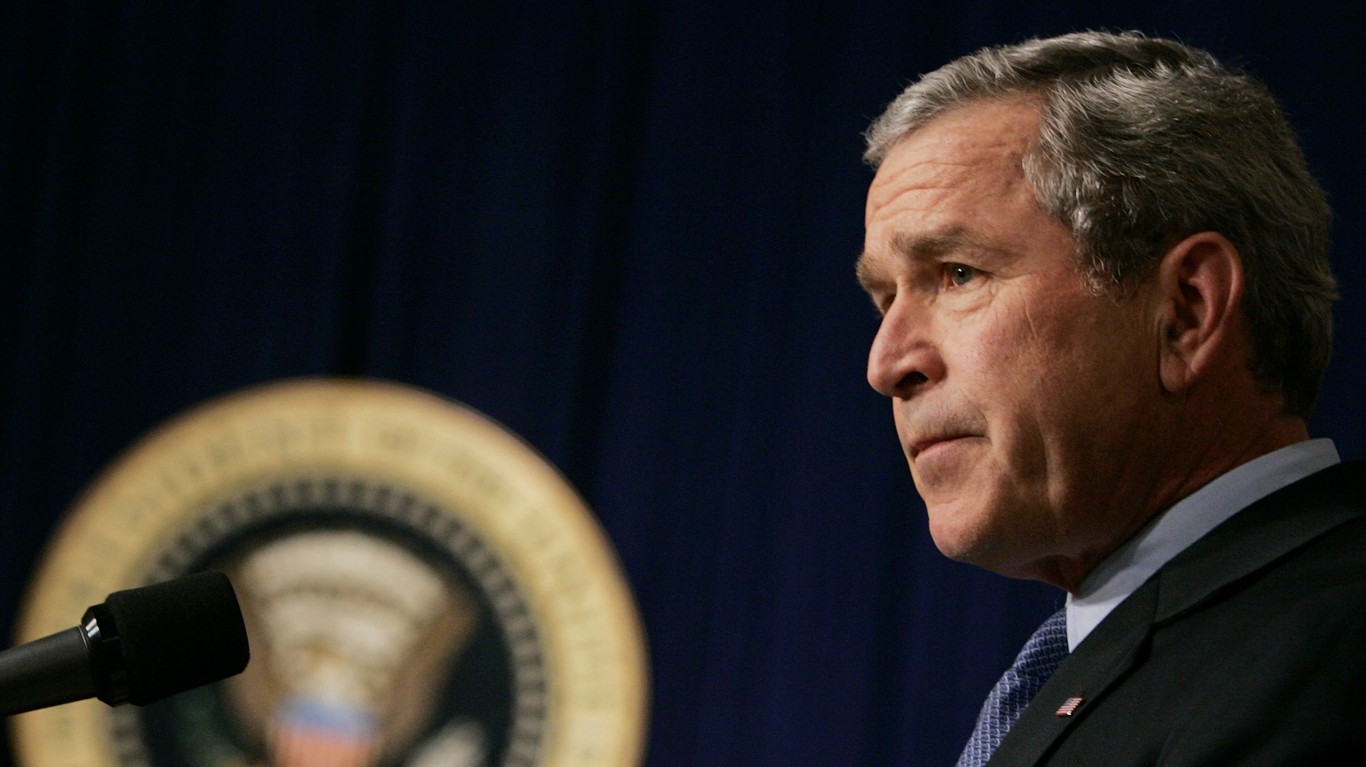

On September 20, 2001, Bush declared the “War on Terror”, which resulted in significant U.S. military operations in Somalia, Yemen, Pakistan, Afghanistan, Libya, Syria, Iraq, and more. It also included severe rhetoric against North Korea, Iran, and Iraq. Bush’s administration repeatedly claimed they had the right to declare preemptive war against countries or groups who might pose a threat to the United States, a policy which quickly became known as the Bush Doctrine. This blatantly offensive policy weakened international support for the United States, a trend that continues today.
Like the War on Drugs before it, the War on Terror has proved to be not only ineffective but profoundly negative in making the situation far worse than it was before.
Bush launched the War in Afghanistan in October of 2001 and the Iraq War in January of 2002. Iraq had no ties to the September 11 attacks and Bush relied on misinformation and outright lies to convince the country and other world leaders to support his invasion.
Bush also launched the President’s Surveillance Program, authorized the torture of suspected terrorists, passed the Patriot Act, and created the Department of Homeland Security.
The post The US Military Budget and the President Who Grew It by 39% appeared first on 24/7 Wall St..