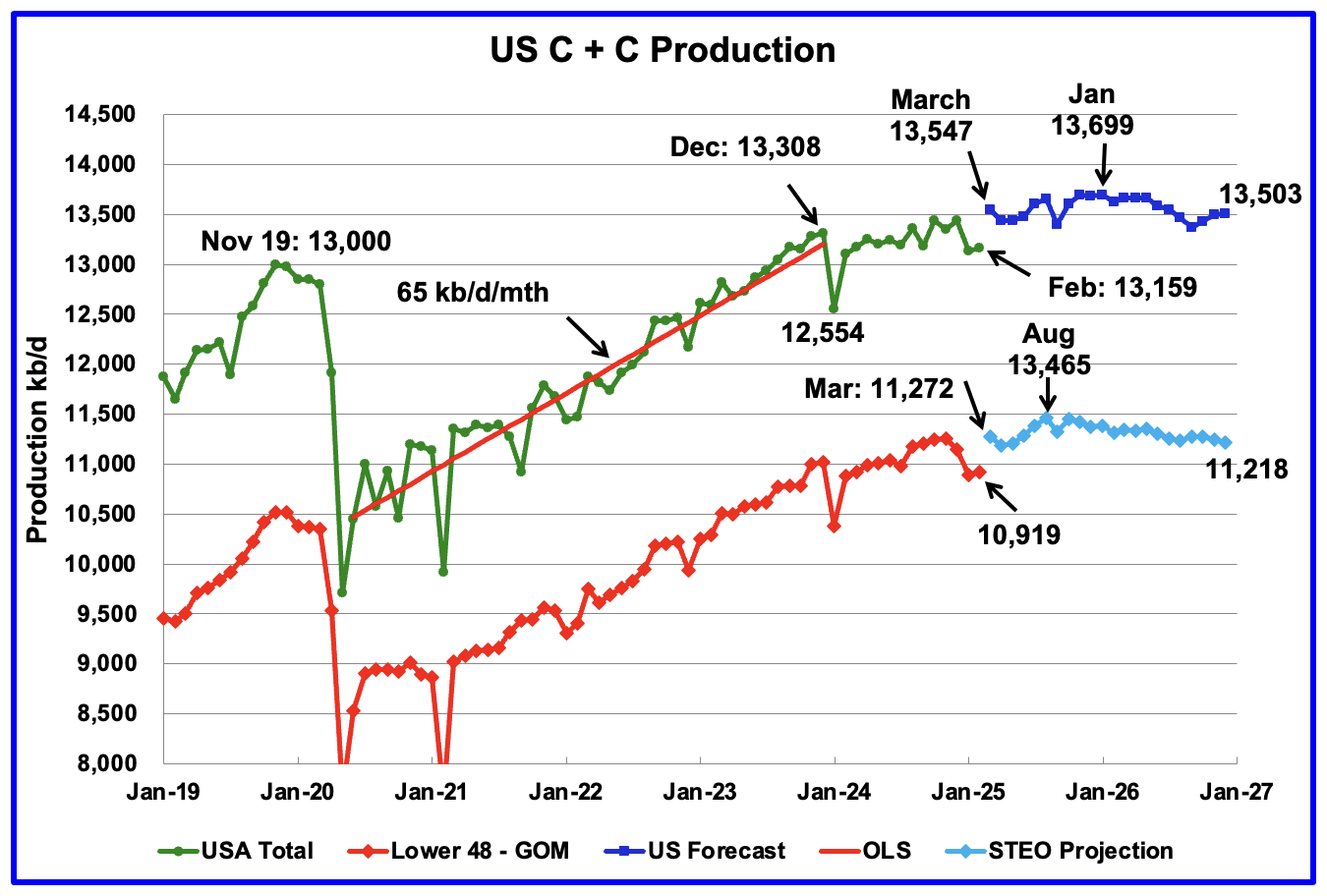
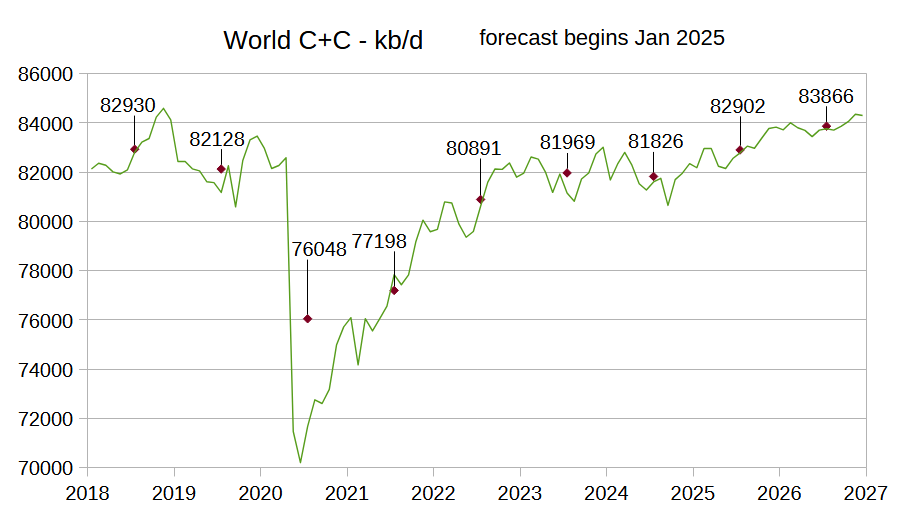
Can SpaceX’s Starship Really Make Mars Colonization Possible?
For decades, humanity has dreamed of establishing human civilization on Mars. This dream is not limited to the public, but has also fascinated scientists and engineers. With the development of SpaceX’s Starship, this dream is looking more like reality than ever before. Yet the question remains—can Starship finally make Mars colonization feasible, or is it […] The post Can SpaceX’s Starship Really Make Mars Colonization Possible? appeared first on 24/7 Wall St..

For decades, humanity has dreamed of establishing human civilization on Mars. This dream is not limited to the public, but has also fascinated scientists and engineers. With the development of SpaceX’s Starship, this dream is looking more like reality than ever before. Yet the question remains—can Starship finally make Mars colonization feasible, or is it still a rocket ride too far?

There are substantial technical, political, and financial obstacles to starting the colonization of Mars within the next few decades. SpaceX is farther along than most toward this ambitious goal.
4 million Americans are set to retire this year. If you want to join them, click here now to see if you’re behind, or ahead. It only takes a minute. (Sponsor)
Key Points
What is SpaceX’s Starship?
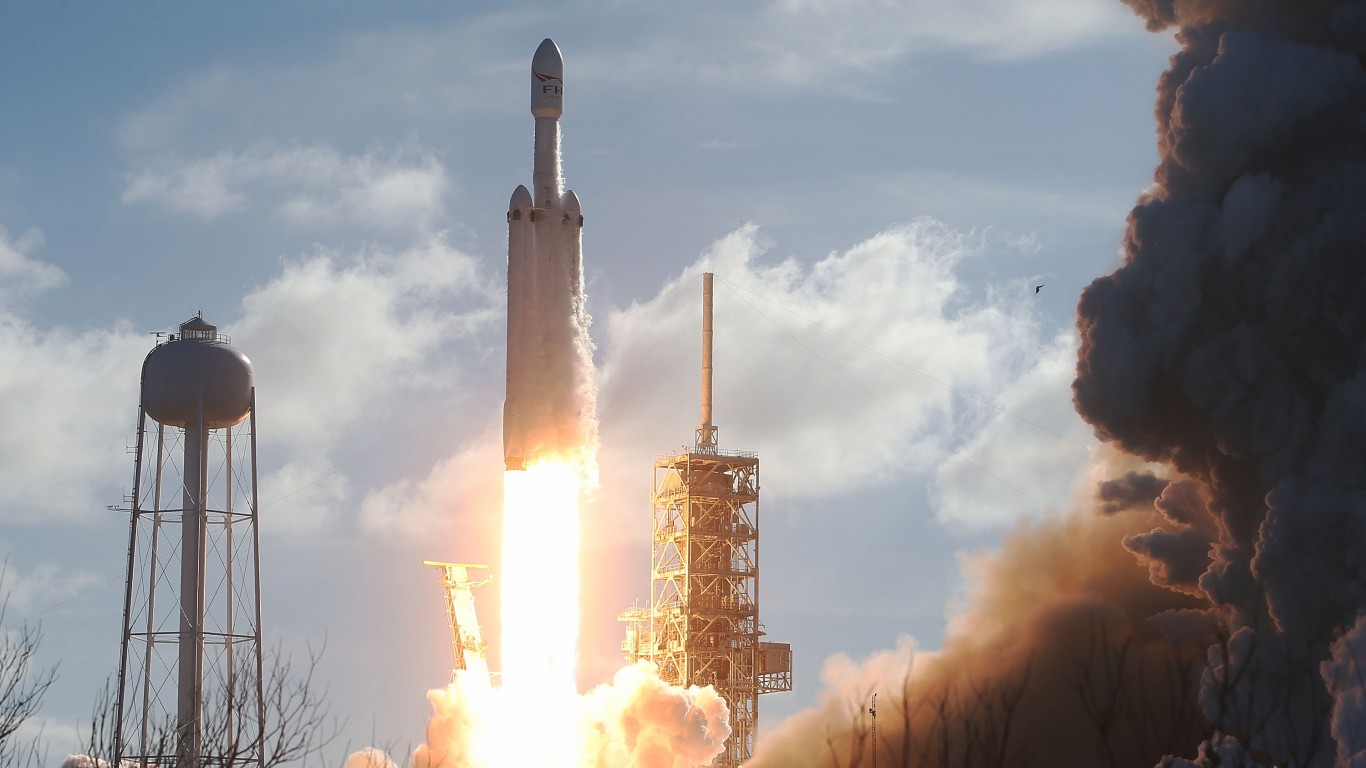

SpaceX’s Starship is a completely reusable launch vehicle with massive lifting capability. It consists of two stages: the Super Heavy booster and the Starship spacecraft. Both of these stages are powered by Raptor engines fueled by liquid methane and oxygen. Starship stands at over 120 meters in height and can carry more than 100 metric tons into orbit. This gives it flexibility for missions as varied as satellite launches, lunar landings, and, yes, Mars colonization.
Starship’s Technical Innovations
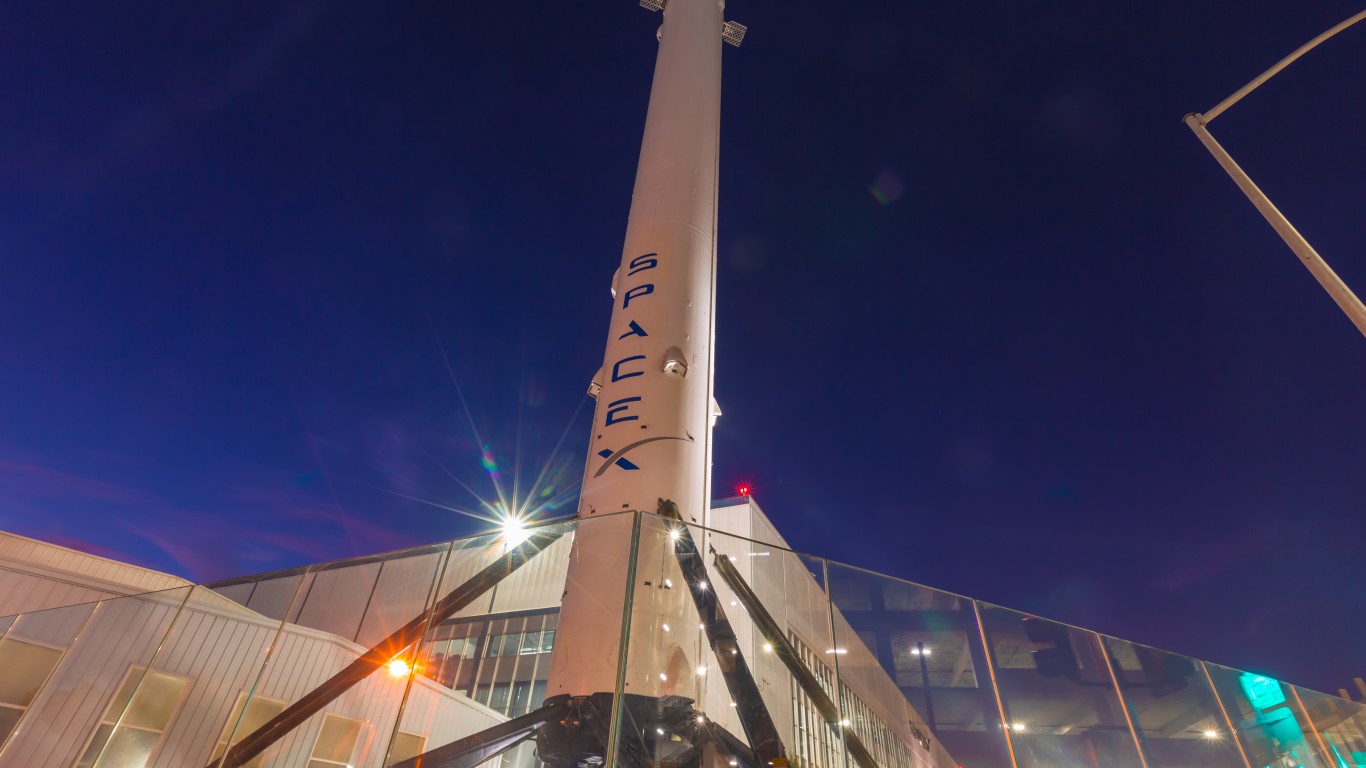

One of Starship’s most significant innovations is its full reusability, reducing wasted material. Its methane fuel can potentially be produced on Mars through what is called in-situ resource utilization, or ISRU. The high payload capacity reduces the number of necessary trips. Finally, the stainless steel construction offers durability, and its modular design allows for iterative improvements and rapid manufacturing without a complete overhaul. All of these features allow SpaceX to drastically reduce their launch costs, and thus increase the frequency of missions.
The Mars Mission Plan

SpaceX has already outlined a possible plan for colonization. Before any humans touch the surface of Mars, uncrewed Starships will deliver infrastructure cargo such as solar power systems, habitats, and resource extraction equipment. The optimal launch windows for these mission occur every 26 months. On the surface, autonomous rovers and robots will prepare for human crews. Once finally on the surface, these humans will expand the outpost and develop self-sufficient systems.
Timeline and Milestones

Elon Musk has set an ambitious timeline for Mars colonization, suggesting the first uncrewed Starship could launch sooner than you might think—by the end of 2026. This would allow possible human landings by 2029 or 2031. Alhough some are understandably skeptical, other experts and leading advocates for Mars colonization such as Robert Zubrin aren’t so sure. He believes that while Musk’s targets are optimistic, a crewed landing by 2031 is plausible if certain technical milestones are met.
Key Challenges to Mars Colonization

Despite Starship’s promise, here are some the key (and formidable) technical milestones that remain:
- Distance and Communication: Mars is 54–401 million km from Earth. For travel, this means a months-long trip. For communication, this results in delays of up to 24 minutes one way.
- Radiation: Mars lacks Earth’s protective magnetic field, exposing potential human settlers to high levels of cosmic radiation. Estimates for a round-trip dose sit at a minimum of 0.66 sieverts—far above safe annual exposure limits.
- Life Support: For long-term life on Mars, reliable systems for necessities such as air, water, food, and waste recycling must be developed and tested rigorously for lengthy use.
- Surface Hazards: Mars’ thin atmosphere, toxic dust, and extreme temperature swings create additional challenges both for human health and technological equipment.
The Role of In-Situ Resource Utilization (ISRU)

One cornerstone of Starship’s colonization plan is ISRU. This means using Martian resources to support life and fuel production, rather than relying on supplies from Earth alone. Starship’s Raptor engines are fueled by liquid methane and oxygen, both of which can be produced on Mars from local materials via the Sabatier reaction. Systems for water and oxygen generation, along with construction materials like sulfur-based concrete, are under development to minimize reliance on continual resupply missions from Earth.
Economic and Logistical Feasibility

Traditional space missions are prohibitively expensive for any large-scale colonization effort. Starship’s reusability and mass production hope to deliver dramatically lower launch costs. Musk himself projects potential costs as low as $2 million per launch in the future. Despite low individual costs, the initial investment for development and production remains high. Any Mars colony achieving true economic sustainability will require robust ISRU and scalable local infrastructure.
Societal and Ethical Considerations

Beyond engineering dilemmas, Mars colonization raises other significant questions:
- Government: SpaceX envisions a self-governing, democratic colony on Mars. However, the legal and ethical frameworks for off-world societies remain unresolved. And of course Earth-based governments and companies making billions of dollars’ worth of investments will want substantial involvement in the development of the colony, and the lion’s share of its profits.
- Safety and risk: Ensuring crew safety during transit and on Mars is a significant concern, especially in the face of technical failures in recent Starship test flights.
- Environmental impact: The introduction of life from Earth onto Mars could irreversibly alter its environment and ecosystem. This in turn raises ethical concerns about planetary protection and human impact. These concerns would be exponentially multiplied if some kind of indigenous life, even at a microscopic level, were discovered on Mars.
Is Starship the Key to Mars?

SpaceX’s Starship is the most advanced and ambitious attempt ever made to enable Mars colonization. Its technical capabilities, cost-reducing innovations, and vision for ISRU make it a plausible method for interplanetary settlement. However, long-term success depends on mounting substantial technical, logistical, and societal hurdles. The question does remain if Starship can continue this pace of development and prove its critical systems in real missions. If it can, Mars colonization is certainly possible possible—though not inevitable—within the coming decades.
The post Can SpaceX’s Starship Really Make Mars Colonization Possible? appeared first on 24/7 Wall St..