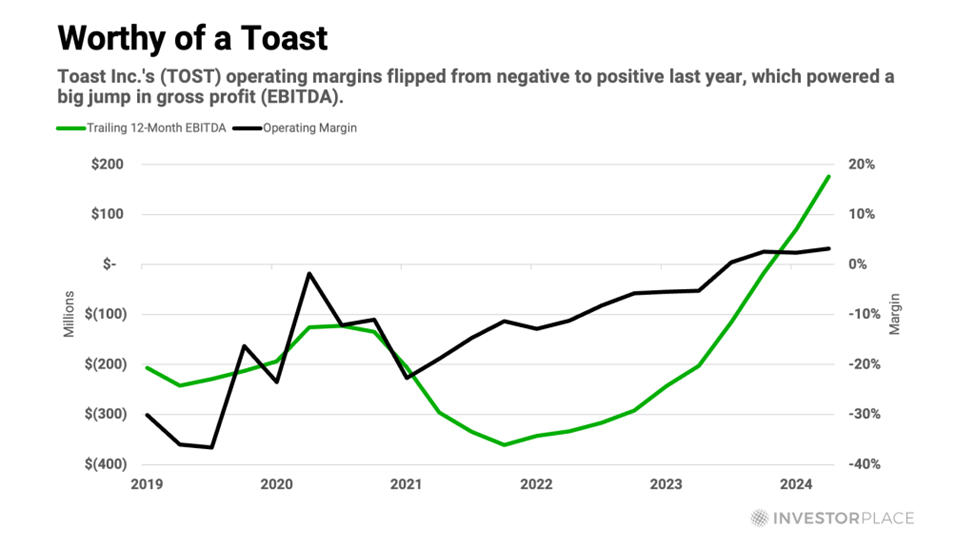
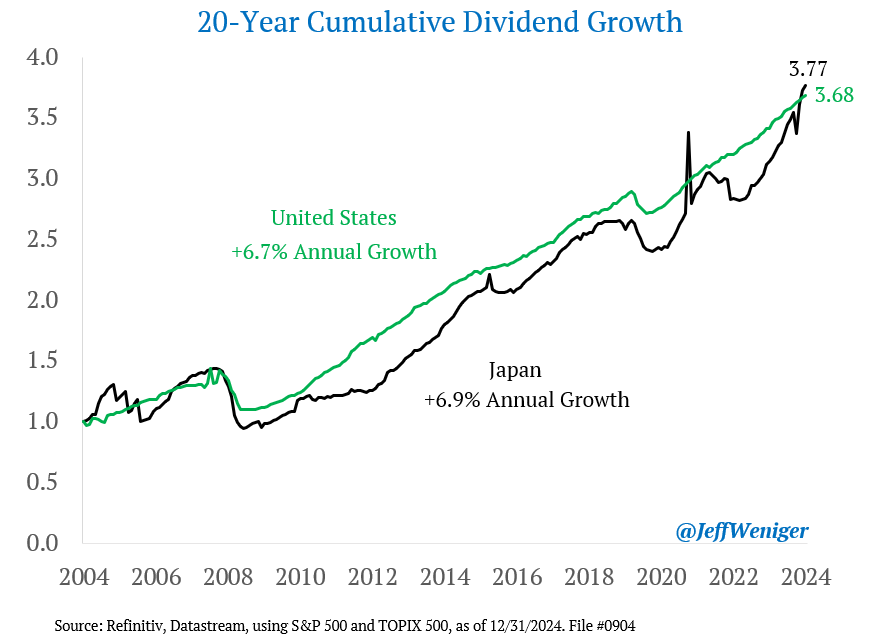
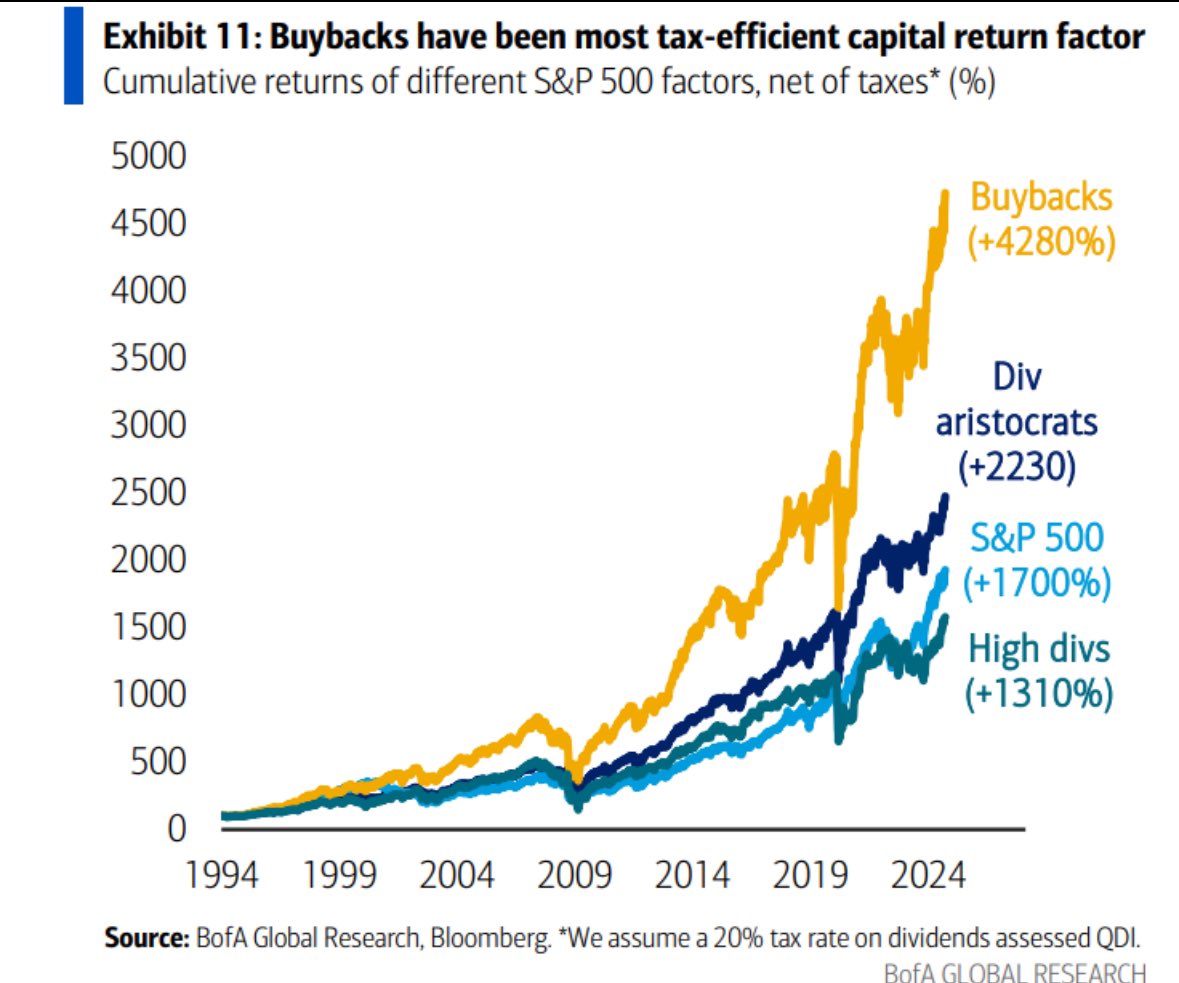
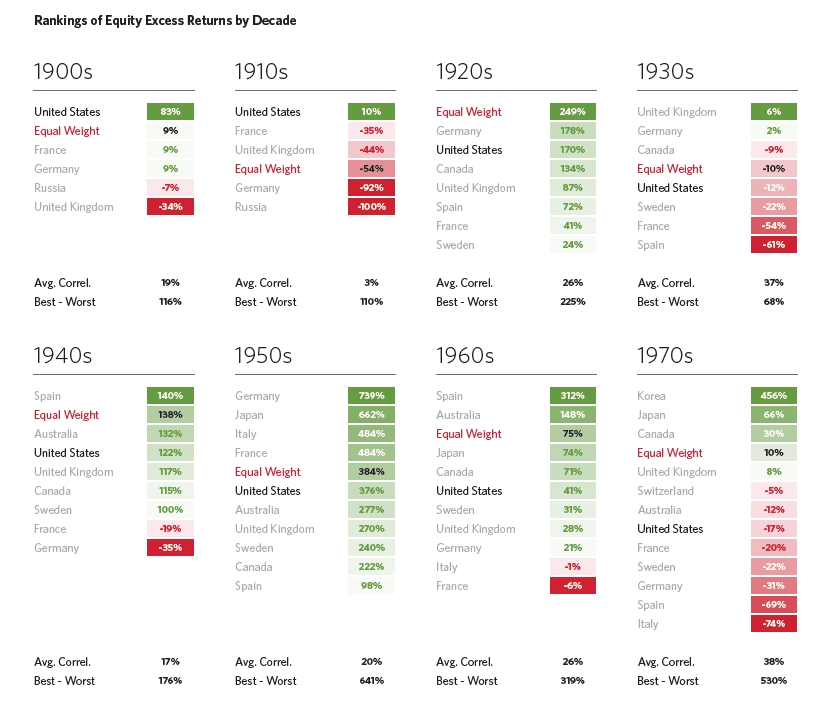
These Are the Factors That Could Affect Your Social Security Payments
More than 10,000 baby boomers are making the transition to becoming retirees on a daily basis in the U.S. alone. The massive demographic shift we’ve seen in recent years has really been quite remarkable, with social security recipients now the most populous group we’ve ever seen as a society. This shift toward an aging population […] The post These Are the Factors That Could Affect Your Social Security Payments appeared first on 24/7 Wall St..

More than 10,000 baby boomers are making the transition to becoming retirees on a daily basis in the U.S. alone. The massive demographic shift we’ve seen in recent years has really been quite remarkable, with social security recipients now the most populous group we’ve ever seen as a society.
Key Points
-
Let’s be honest, there are a number of different factors that can affect social security payments in retirement.
-
Here are a few of the most prominent and important factors investors may want to consider.
-
Are you ahead, or behind on retirement? SmartAsset’s free tool can match you with a financial advisor in minutes to help you answer that today. Each advisor has been carefully vetted, and must act in your best interests. If you’ve saved and built a substantial nest egg for you and your family; get started by clicking here.(Sponsor)
This shift toward an aging population has had a number of impacts on society as a whole. From the government’s perspective, many of the social safety net line items (which were put in place largely in 1960s, when baby boomers were young and in their prime years) are set to pay out for those who have worked their entire lives, are quite expensive. And there are increased concerns that key government programs like Medicare and social security as a whole may not be around for the coming generation (given how the system is currently structured).
However, that’s not to say there aren’t factors retirees shouldn’t pay attention to right now that can influence the size of their monthly social security checks. For those nearing or already in retirement, here are five key factors I think are worth focusing on right now.
Work History and Earnings

Every individual and household’s social security payments will vary slightly, given the formula that goes into calculating how much one should receive in retirement. This calculation is focused on determining how much an individual contributed to social security over the course of their lifetime, taking the highest 35 earning years as the foundation for an individual’s social security payments. The more one earned in his or her lifetime (and therefore contributed to social security), the more than individual will receive in retirement. And for those who were at or near the social security maximum (there’s a limit on how much individuals must pay out of their paychecks to social security) for decades (up to 35 years), it’s possible to achieve the top end of social security payments in retirement.
Additionally, it’s worth noting that the age at which you choose to claim benefits also matters. Claiming early reduces your monthly check, while delaying past your full retirement age (FRA) can increase these payments substantially. That gets us to the next key factor worth considering.
Age When Claiming Benefits

So, you’ve worked your whole life and contributed to social security at a realtively high rate for 35 years. Great.
Now, the question is: when to start taking distributions? For those who have achieved this high-earner status and are now 62 (the earliest age individuals can choose to take social security), the question becomes not how to maximize one’s distributions from an earnings history standpoint, but from how early one wants to begin taking distributions.
Full retirement age (FRA) is now 67, so by taking distributions early at 62, retirees could receive a permanent reduction in benefits of up to 30% by doing so. Those who choose to wait until 70 could boos their distributions by 8% (over and above the 30% they’d get back from not retiring early). For those who do not need immediate income and expect to live a long time, that’s a great deal.
Of course, we never know when we’re going to die, so this is a difficult factor to consider. But for those who are healthy and feel great, extending out social security payments and having them come in at more meaningful levels can be important.
Spousal Benefits

In addition to one’s work history and the age at which seniors choose to take social security, spousal benefits can also be a way in Social Security planning, providing an additional income stream for eligible spouses and ex-spouses. To qualify, retirees must be at least 62 years old or caring for a child under 16 or with a disability. Married individuals must have been married for at least one year, while divorced individuals must have had a 10-year marriage to claim benefits from an ex-spouse.
The maximum spousal benefit is 50% of the higher-earning spouse’s full retirement benefit, but claiming before full retirement age (FRA) reduces this amount, with early filers receiving as little as 32.5%. Unlike standard retirement benefits, spousal benefits do not increase beyond FRA. Claiming spousal benefits does not reduce the primary beneficiary’s payments, and if eligible for both personal and spousal benefits, Social Security provides the higher amount, not a combination of both.
Inflation Adjustments

As we’ve seen in recent years, inflation is real, and has a meaningful impact of everything tied to our daily lives. As the cost of everything increases, it can be harder and harder for retirees to make ends meet, considering the fixed nature of social security payments.
That said, inflation Adjustments do play a crucial role in Social Security payments through the cost-of-living adjustment (COLA), ensuring that benefits keep pace with inflation. The Social Security Administration (SSA) determines COLA annually based on the Consumer Price Index for Urban Wage Earners and Clerical Workers (CPI-W). If inflation rises, a COLA is applied to Social Security benefits the following year.
For example, the COLA for 2024 was 3.2%, while the projected adjustment for 2025 is 2.5%, reflecting lower inflation rates. These adjustments help protect retirees’ purchasing power, preventing benefits from being eroded by rising prices.
However, COLA may not fully cover cost increases in essential expenses like healthcare and Medicare premiums, which often outpace inflation. Over time, if inflation consistently exceeds cost of living adjustments, beneficiaries may struggle with rising living costs.
Economic Conditions

Economic conditions play a vital role in shaping Social Security payments by influencing both funding sources and overall program sustainability. Payroll taxes, which fund Social Security, are directly tied to employment and wage levels. During economic downturns, higher unemployment and lower wages reduce payroll tax revenue, potentially straining Social Security’s ability to meet obligations. While economic growth can improve the program’s financial outlook, it alone may not offset long-term funding shortfalls caused by an aging population and increasing benefit claims.
Additionally, economic stimulus measures can impact Social Security indirectly by reducing unemployment rates, which may decrease the number of disability benefit applications. However, the effectiveness of these measures depends on labor market conditions and workforce participation.
The post These Are the Factors That Could Affect Your Social Security Payments appeared first on 24/7 Wall St..