How Much Firepower Does the U.S. Space Force Actually Have?
When the U.S. government decided to create the Space Force it got plenty of news coverage, but it has faded from the news cycle ever since. Most people might not know exactly what the Space Force does or how powerful it is. We looked into what the Space Force has been up to since its […] The post How Much Firepower Does the U.S. Space Force Actually Have? appeared first on 24/7 Wall St..

When the U.S. government decided to create the Space Force it got plenty of news coverage, but it has faded from the news cycle ever since. Most people might not know exactly what the Space Force does or how powerful it is.
Key Points
-
The U.S. Space Force is a branch under the department of the Air Force and uses much of the Air Force’s military hardware and capabilities.
-
The Space Force isn’t designed to engage in direct combat, but manages the U.S.’s satellites and missile defense systems, among other space-related technology.
-
4 million Americans are set to retire this year. If you want to join them, click here now to see if you’re behind, or ahead. It only takes a minute. (Sponsor)
We looked into what the Space Force has been up to since its creation and what weapons and hardware have been given to it to accomplish those goals. Here is everything we know about the U.S. Space Force.
Background on Space Force

Despite strong opposition from the Air Force and the Defense Department, Congress has repeatedly tried to expand the military capabilities of the U.S. for decades. In 2018, President Trump publicly endorsed the idea and told the Defense Department to create plans for what would become the Space Force.
Technically, the Space Force is a branch of the Air Force and is the sixth armed service, but it is not an independent department.
As a result, much of the technology, funding, and capabilities used by the Space Force come from the Air Force budget and existing arsenal. The Air Force also continues to maintain several systems the Space Force relies on.
Military Bases
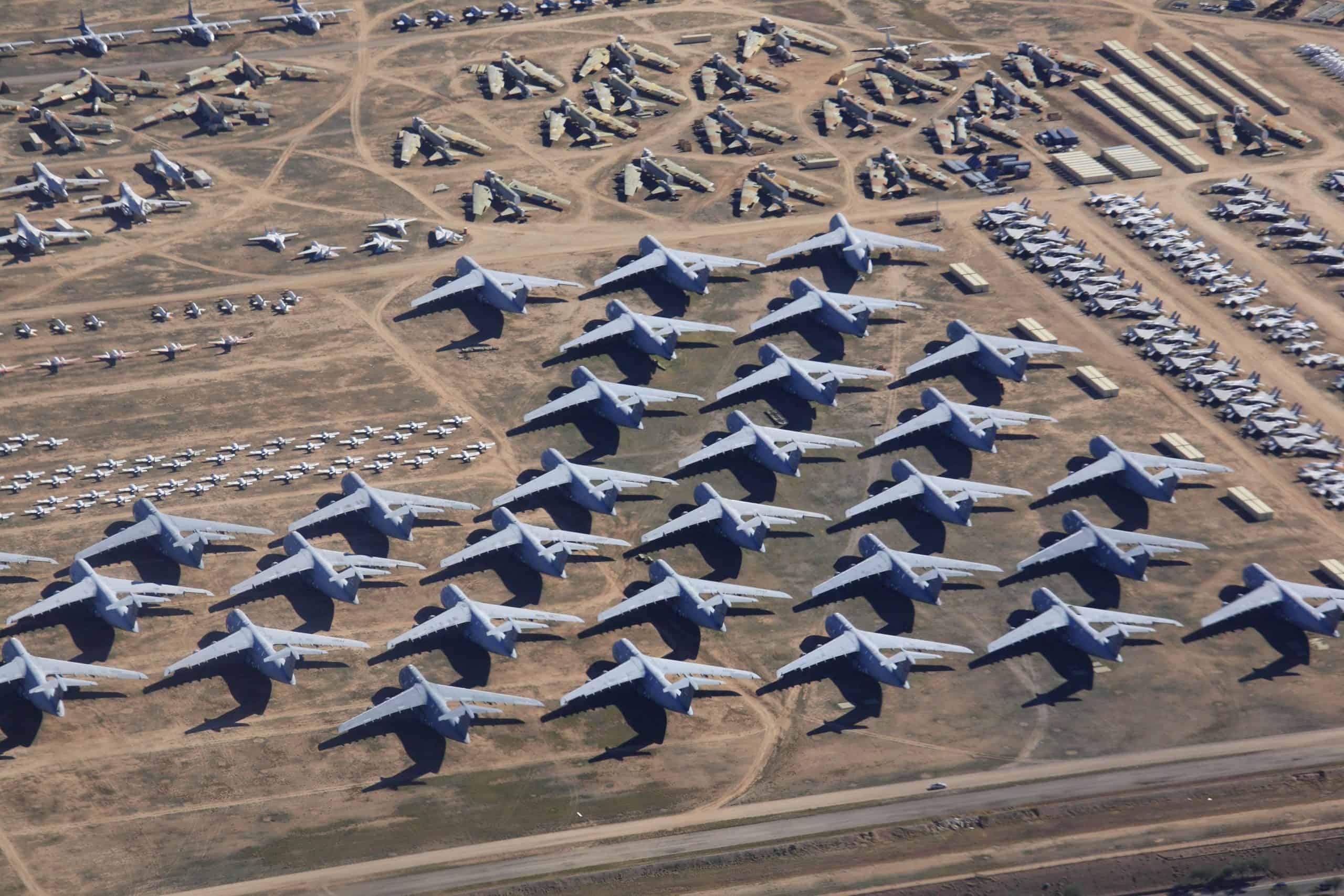

The Space Force is headquartered in Washington D.C. and owns and operates 46 different bases and installations across the United States and other countries. Most of these locations are land-based radar stations and satellite dishes for observing objects in Earth’s orbit or detecting missiles after launch.
Since the Space Force doesn’t actually have a division that will engage in combat with other forces, it has no training bases or significant amounts of military arms.
Spacecraft

The Space Force has at least 17 different spacecraft systems or satellite programs, with most having numerous satellites, while some have an unknown number with unknown capabilities. Most of these are used for space surveillance, satellite communications, environmental monitoring, missile warning, navigation and timing, battlefield support, spying, orbital testing, and domestic surveillance.
This includes the Global Positioning System that companies around the world use for precise location tracking. This system has 32 satellites in orbit.
The Wideband Global SATCOM system includes 10 satellites and allows high-capacity communications between the U.S., Canadian, and Australian military forces.
The Advanced Extremely High Frequency system includes six satellites and facilitates secure military communication for the U.S. and a number of its military allies including the U.K., the Netherlands, Canada, and more.
The Geosynchronous Space Situational Awareness Program includes six satellites and is used for spying and surveillance of targets abroad and in the United States. It is also known as HORNET.
The Milstar system includes five satellites that provide jam-proof communications for all U.S. military forces.
The Space-Based Infrared System includes 12 satellites and provides missile warning systems, battlespace analysis, and intelligence-gathering capabilities.
Naturally, there are other satellite-based systems and capabilities that are not public knowledge or are classified.
Space Systems

In order to operate and maintain a significant presence in space, the Space Force also manages a number of ground-based systems.
The AN/FPS-85 space surveillance system is an array of radar dishes for identifying man-made objects in Earth’s orbit.
The C-Band Space Surveillance Radar System is an array of dishes in Australia that provide radio transmission to military fleets in the region. It is the strongest radio transmission system in the Southern Hemisphere.
The Cobra Dane system is located in Alaska and was built in the 1970s to monitor for missiles launched from the Soviet Union.
The Ground-Based Electro-Optical Deep Space Surveillance system identifies and tracks artificial satellites in Earth’s orbit.
The Long Range Discrimination Radar is another missile defense and space surveillance system that forms part of the U.S. Ground-Based Midcourse Missile Defense anti-ballistic missile system.
The Perimeter Acquisition Radar Attack Characterization System is an array of radar systems in North Dakota designed to be an early missile warning system and space surveillance system.
The Satellite Control Network is the system of personnel and technology that support, operate, maintain, and control the majority of satellites under the Department of Defense’s jurisdiction.
The Space Fence system is another early warning system to identify and track artificial satellites in Earth’s orbit.
The Space Surveillance Telescope is located in Australia and is used to detect and track natural and artificial objects in space.
The Upgraded Early Warning Radar is yet another missile warning system that is also used to identify and track artificial satellites in Earth’s orbit.
Launch Vehicles
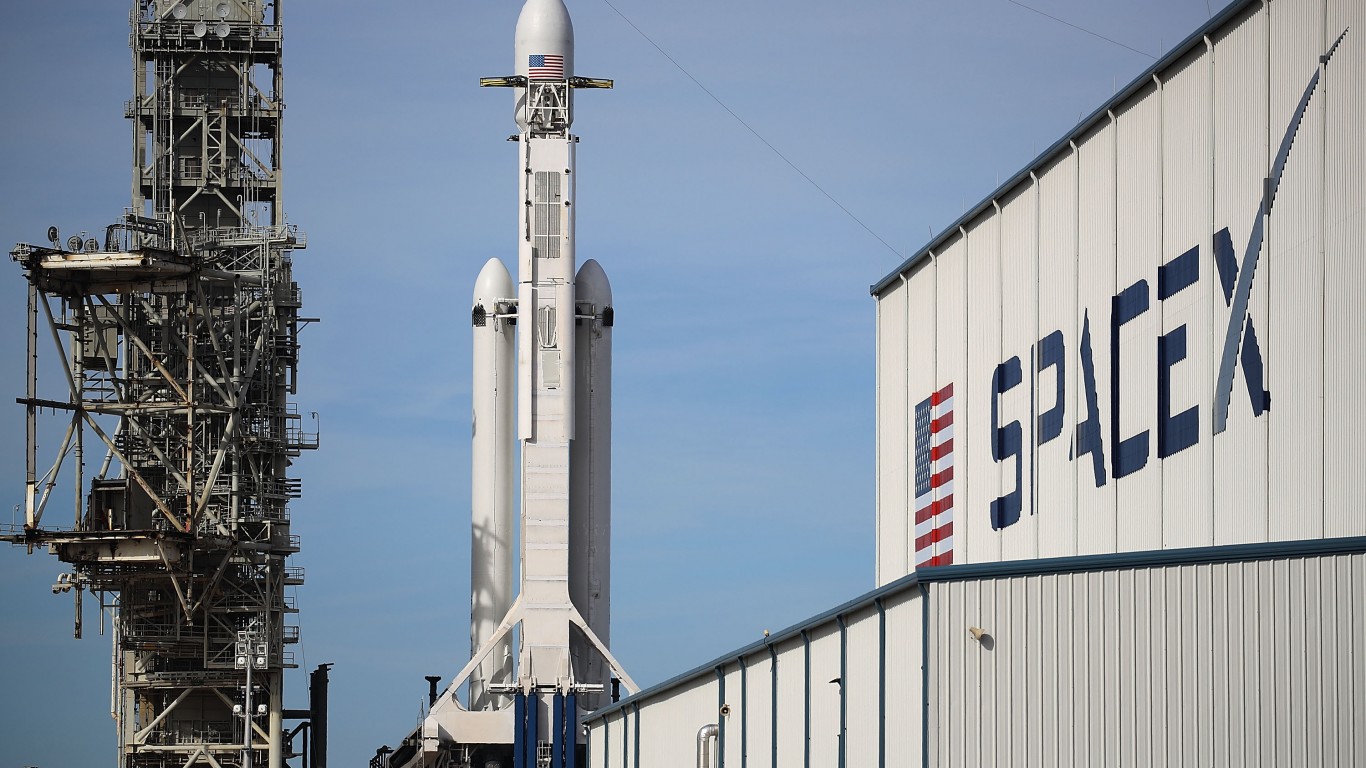

In order to get satellites and other things into orbit, the U.S. Space Force makes use of a number of different launch vehicles depending on the size of the payload, the availability of the launch vehicles, the cost associated with a certain program, and other factors.
The Atlas V is the longest-serving rocket in the United States and is the fifth generation of the famous Atlas launch vehicle line. It costs between $110 million and $153 million to launch the Atlas V depending on the weight of the cargo.
The Electron was created in partnership with a New Zealand company and is the third-most-popular small-lift launch vehicle in the world.
The Falcon 9 is a launch vehicle developed by SpaceX with significant money from the U.S. government. It is a medium to heavy-lift launch vehicle and costs around $70 million to launch.
The Falcon Heavy is a super heavy-lift launch vehicle that is partially reusable like the Falcon 9 and the Electron. It is also designed and manufactured by SpaceX. It costs around $150 million to launch the Falcon Heavy.
The Pegasus launch vehicle is a small-lift option that is launched from an airplane while in flight. It is the first privately developed launch vehicle and costs around $40 million per launch.
The post How Much Firepower Does the U.S. Space Force Actually Have? appeared first on 24/7 Wall St..