NASA Explores Earth Science with New Navigational System
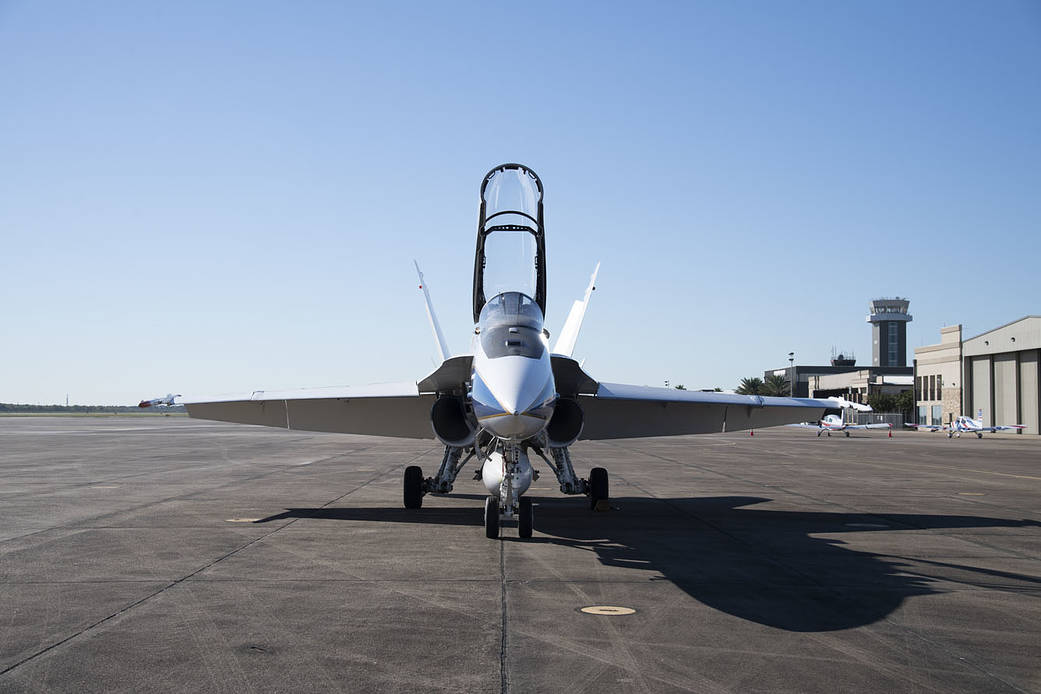
NASA and its partners recently tested an aircraft guidance system that could help planes maintain a precise course even while flying at high speeds up to 500 mph. The instrument is Soxnav, the culmination of more than 30 years of development of aircraft navigation systems. NASA’s G-IV aircraft flew its first mission to test this […]

3 min read
Preparations for Next Moonwalk Simulations Underway (and Underwater)
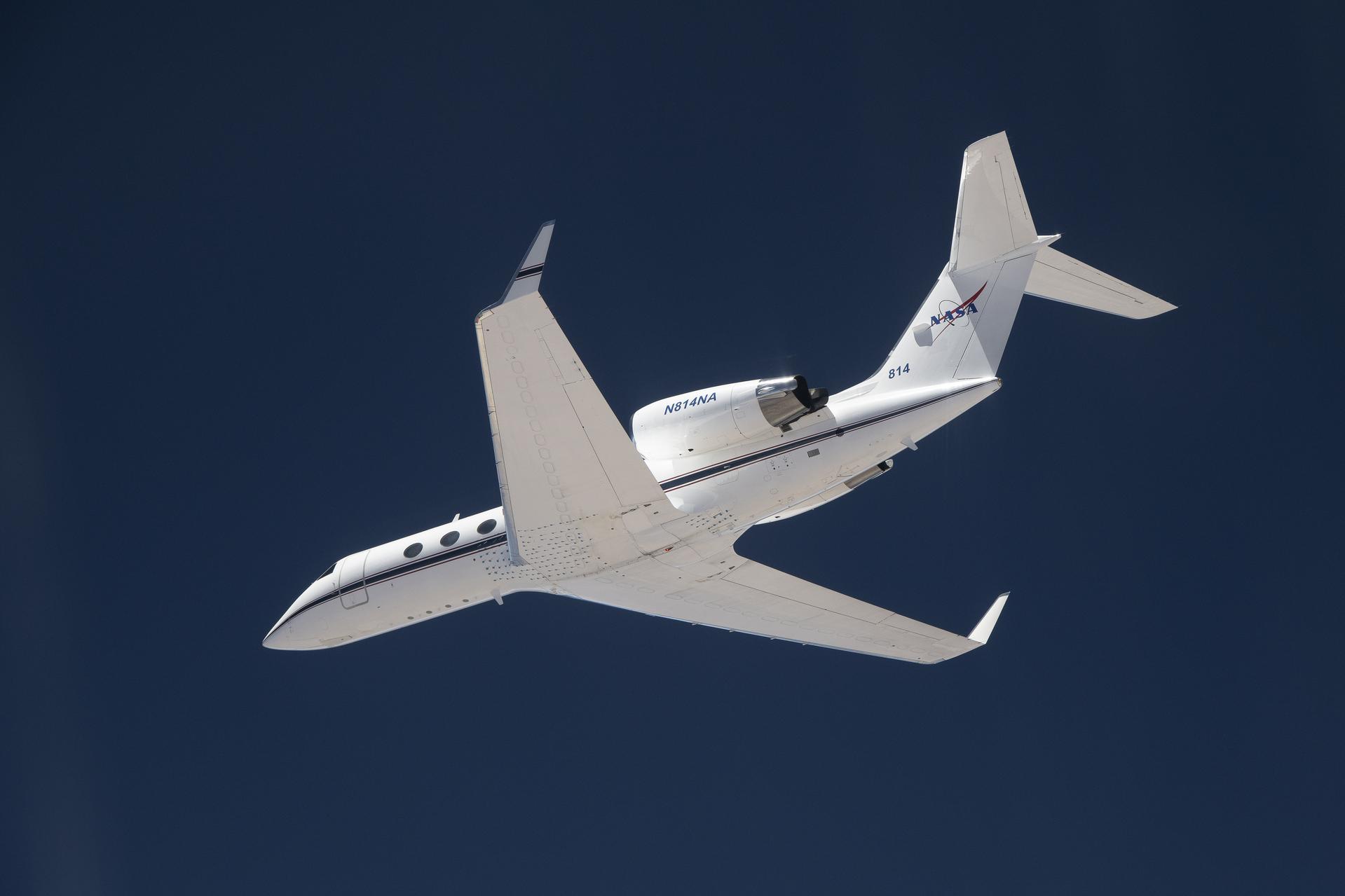

NASA and its partners recently tested an aircraft guidance system that could help planes maintain a precise course even while flying at high speeds up to 500 mph. The instrument is Soxnav, the culmination of more than 30 years of development of aircraft navigation systems.
NASA’s G-IV aircraft flew its first mission to test this navigational system from NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California, in December 2024. The team was composed of engineers from NASA Armstrong, NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California, and the Bay Area Environmental Research Institute (BAERI) in California’s Silicon Valley.
“The objective was to demonstrate this new system can keep a high-speed aircraft within just a few feet of its target track, and to keep it there better than 90% of the time,” said John Sonntag, BAERI independent consultant co-developer of Soxnav.
With 3D automated steering guidance, Soxnav provides pilots with a precision approach aid for landing in poor visibility. Previous generations of navigational systems laid the technical baseline for Soxnav’s modern, compact, and automated iteration.
“The G-IV is currently equipped with a standard autopilot system,” said Joe Piotrowski Jr., operations engineer for the G-IV. “But Soxnav will be able to create the exact level flight required for Next Generation Airborne Synthetic Aperture Radar (AirSAR-NG) mission success.”
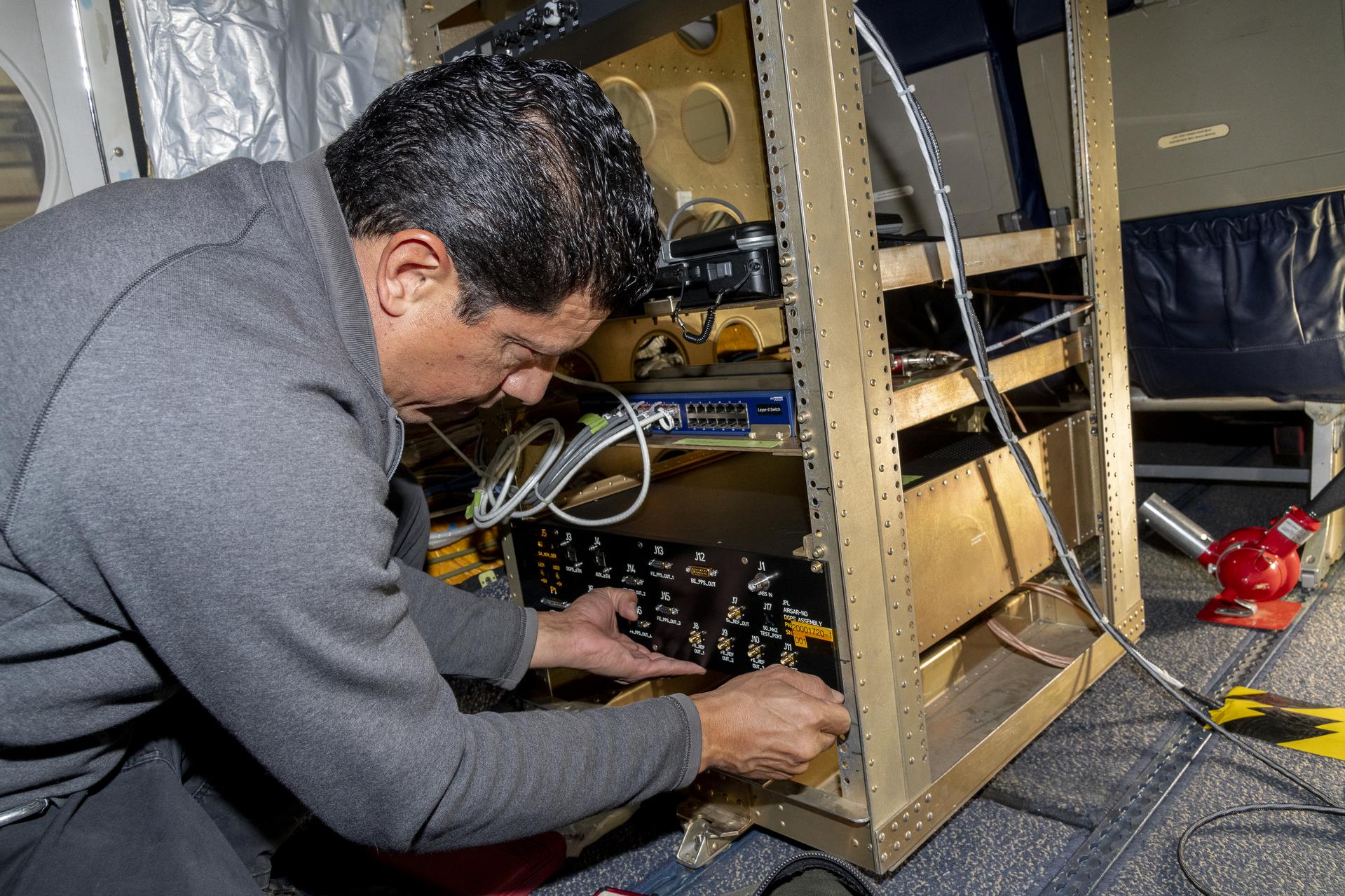

Guided by Soxnav, the G-IV may be able to deliver better, more abundant, and less expensive scientific information. For instance, the navigation tool optimizes observations by AirSAR-NG, an instrument that uses three radars simultaneously to observe subtle changes in the Earth’s surface. Together with the Soxnav system, these three radars provide enhanced and more accurate data about Earth science.
“With the data that can be collected from science flights equipped with the Soxnav instrument, NASA can provide the general public with better support for natural disasters, tracking of food and water supplies, as well as general Earth data about how the environment is changing,” Piotrowski said.
Ultimately, this economical flight guidance system is intended to be used by a variety of aircraft types and support a variety of present and future airborne sensors. “The Soxnav system is important for all of NASA’s Airborne Science platforms,” said Fran Becker, project manager for the G-IV AirSAR-NG project at NASA Armstrong. “The intent is for the system to be utilized by any airborne science platform and satisfy each mission’s goals for data collection.”
In conjunction with the other instruments outfitting the fleet of airborne science aircraft, Soxnav facilitates the generation of more abundant and higher quality scientific data about planet Earth. With extreme weather events becoming increasingly common, quality Earth science data can improve our understanding of our home planet to address the challenges we face today, and to prepare for future weather events.
“Soxnav enables better data collection for people who can use that information to safeguard and improve the lives of future generations,” Sonntag said.