Can You Guess Which State Has the Weakest Gun Control Laws?
In March of 2025, a state appellate court decided that gun control measure 114 is constitutional. Now, an Oregon Supreme Court has agreed to review the previous decision. Measure 114 was just barely approved by a vote back in November of 2022. However, it faced legal challenges from 2 Harney County gun owners that argued […] The post Can You Guess Which State Has the Weakest Gun Control Laws? appeared first on 24/7 Wall St..

In March of 2025, a state appellate court decided that gun control measure 114 is constitutional. Now, an Oregon Supreme Court has agreed to review the previous decision. Measure 114 was just barely approved by a vote back in November of 2022. However, it faced legal challenges from 2 Harney County gun owners that argued against its constitutionality, which prevented it going into effect. The measure introduces several points, including placing a limit on gun magazine capacity at 10 rounds, requiring permits for gun purchases, and mandating background checks for private purchases. The measure is backed by the Oregon attorney general’s office who describes it as reasonable and necessary for public safety.
Guns are big in America, in both size and popularity. As more gun-related incidents have taken place in recent years, gun control regulation takes center stage. The ‘gun-control’ conversation can be complicated, as it pits citizen safety against our Second Amendment rights. Those who advocate for stricter gun control are proponents of background checks and limits on assault rifles.
Texas residents are strongly attached to their guns, making this state weak on gun regulation. In fact, many of the state’s laws support open carry without a permit of any kind. As gun advocates seek to allow guns on college campuses, safety-centric individuals are focused on reeling in such lax legislation.
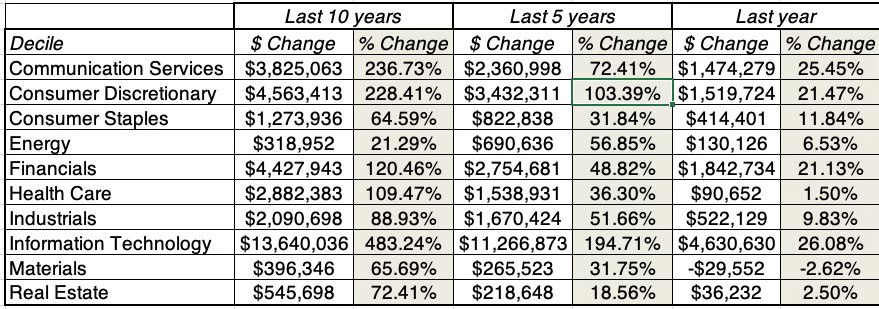
24/7 Wall St. reviewed Texas’ approach to 14 key gun control policy areas using data from the Giffords Law Center, a gun violence prevention group, finding that Texas has some of the weakest gun control laws in the country. Accounting for a wide range of policies at the disposal of state governments — including assault-style weapon and high-capacity magazine bans, universal background check laws, waiting periods, and restrictions on firearms in public — Gifford’s Law Center assigned Texas a letter grade of “F”, on an A-F scale, for the strength of its gun control policies. Laws on this list are not exhaustive and only represent broad guidelines. Also, legal nuances can vary at the state and local levels.
This post was updated on June 22, 2025 to include information about Oregon’s gun measure.
Why It Matters

With the exception of some modest revisions to background check protocols, the U.S. has not implemented any meaningful gun control reform in decades. Still, state governments also have the authority to enact their own policies, resulting in a patchwork of gun laws across the 50 states. Currently, Texas ranks as having some of the weakest state-level firearm regulations in the country.
Universal background check laws

- State policy: Under federal law, all gun buyers must undergo a background check before obtaining a firearm from a licensed retailer — but transfers made from unlicensed retailers are exempt from background check requirements. While many states have closed this loophole with universal background check laws, Texas has not.
Mental health reporting

- State policy: Texas is required to report individuals involuntarily committed to undergo mental health treatment in an inpatient setting to federal background check databases as well as those who are living with a guardian because they cannot manage their own affairs. However, the state is not required to report those being involuntarily treated in outpatient facilities.
Concealed carry of a firearm

- State policy: No permit required to carry a concealed firearm in certain public places in Texas.
Handgun open carry regulations

- State policy: Lawful gun owners are generally permitted to open-carry a handgun in certain public places in Texas, provided the firearm is secured in a holster.
Long gun open carry regulations

- State policy: In Texas, long guns may be openly carried in certain public places, as long as the firearm is not deliberately used in a manner to deliberately cause alarm.
Stand your ground laws

- State policy: Use of deadly force is permitted in public, if necessary, to prevent death or serious bodily harm — even if it is possible to step away from the incident.
Guns in schools

- State policy: In Texas, firearms can be carried in K-12 schools by school security officers, teachers, and other school employees, provided the individual is a designated school marshal or is otherwise authorized to manage school security.
Mandatory waiting periods for firearm purchases

- State policy: There is no mandatory waiting period for firearm purchases in Texas.
Assault-style weapons

- State policy: Assault-style weapons, like those modeled after AK-47 or M-16 military rifles, are not regulated in Texas.
High-capacity magazines

- State policy: Texas does not restrict high-capacity magazines.
Licensing requirements

- State policy: Gun owners or prospective buyers do not need to obtain a permit in Texas.
State-level prohibitions on who can own firearms

- State policy: In Texas, individuals struggling with alcohol abuse can have their access to firearms restricted.
Minimum age requirements for handguns

- State policy: In Texas, individuals must be at least 18 years old to purchase a handgun. The state does not set a minimum age requirement for possession of a handgun.
Minimum age requirements for long guns

- State policy: In Texas, individuals must be at least 18 years old to purchase a long gun, like a rifle or shotgun. The state does not set a minimum age requirement for possession of a long gun.
The post Can You Guess Which State Has the Weakest Gun Control Laws? appeared first on 24/7 Wall St..