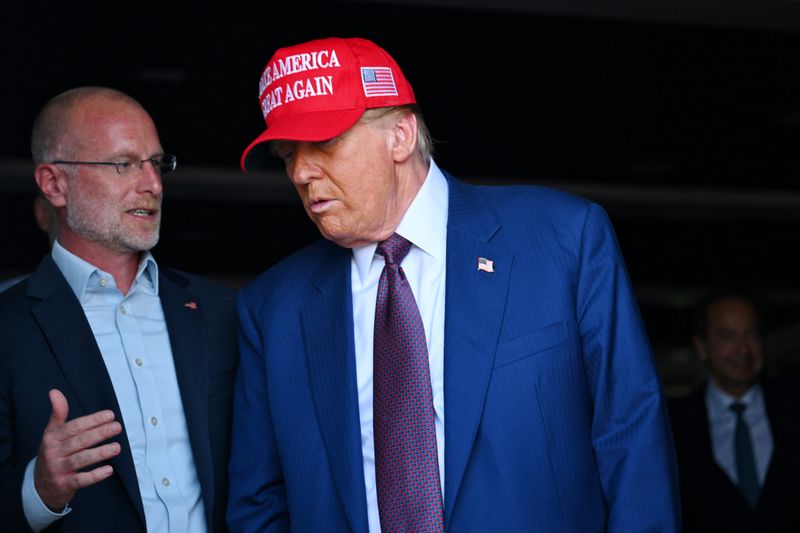
After denying reports of BP takeover, Shell is legally barred from making an offer for six months—and there are no other suitors in sight
A theoretical Shell-BP combination would carry debt and anti-trust issues while requiring greater layoffs and divestments.

Shell doubled down on its denial of acquiring rival BP, claiming it has “no intention” of making an offer while invoking a U.K. law that forbids Shell from bidding on BP during the next six months with few exceptions.
The June 26 news comes after reports that Shell entered early talks to buy BP in what would easily represent the largest energy deal of the century—if not ever. But with Shell seemingly stepping aside to focus on internal performance—at least for now—financially struggling BP is left without any other clear suitors as the British energy giant seeks a turnaround following its “hard reset” through cost cuts, greater fossil fuel investments, and renewables divestments.
“In response to recent media speculation, Shell wishes to clarify that it has not been actively considering making an offer for BP and confirms it has not made an approach to, and no talks have taken place with BP with regards to a possible offer,” Shell said in a prepared statement.
The statement was issued under a rule in the U.K.’s takeover code that bans backtracking on its claims for the next six months unless Shell has the agreement of BP’s board, another company bids on BP, or there’s a material change in circumstances. Citing the code allows Shell to better reassure its investors that it is focused on its strategy and not massive, debt-laden acquisitions at this moment.
BP declined comment.
Shell’s statement followed a June 25 report from The Wall Street Journal that Shell was in early talks to potentially buy BP, which also came after previous speculation and reports that Shell was studying a possible deal to combine two of the biggest Big Oil giants.
“For now, any takeover of BP by Shell will be a 2026 story, and is unlikely to happen in 2025,” said Kathleen Brooks, research director for the XTB brokerage house. “BP’s share price is still underperforming its global peers and, now that Shell is out of the running as a potential buyer, we do not see BP repairing its position in the coming weeks or months.”
Big deal-making challenges
Indeed, only a small handful of companies could afford to acquire BP with its large, but underperforming, $80 billion market cap. London-based Shell is the most obvious, but the others—Exxon Mobil and Chevron—are coming off or are amid massive acquisitions of their own. And the U.S. supermajors could have greater anti-trust challenges even if they were interested, said Deborah Byers, senior adviser at the energy research and investment firm Veriten.
Of note, is that Shell switched its headquarters to London from the Netherlands three years ago, changing the Royal Dutch Shell name to Shell PLC.
“I think the U.K. government would block a foreign purchase. Maybe Shell is a white knight, and they would be OK from a regulatory standpoint in the U.K.,” Byers said. “You would think the U.K. would not accept anyone other than Shell—even a U.S. major.”
And that’s not accounting for all of the debt, headcount, and nation-by-nation regulatory approvals Shell would have to go through to acquire another global energy supermajor, Byers said. Shell and BP each employ nearly 100,000 people, although they are both currently downsizing, while leaner Exxon Mobil, for instance, has about 60,000 employees. Then, Shell would need to undergo a prolonged period of divestments to satisfy the balance sheet and anti-trust issues in different nations.
“Why would [Shell] want to do that?” Byers said. “Do shareholders really want growth? Or do they just want capital discipline and returns—either dividends or buybacks? It’s been a while since anyone has been rewarded for growth in this sector.”
She said BP shareholders “have to be patient” as it attempts its financial reset, acknowledging that BP is dealing with investor activism from Elliott Investment Management and others.
“The challenge is what is that patience timeline?” Byers said. “Their patience might be two or three quarters, but they probably need a couple of years to really work through some of these issues that are strategic pivots.”
Likewise, in a recent analyst note, Biraj Borkhataria of RBC Capital Markets, said BP’s debt profile, including remaining liabilities from the 2010 Deepwater Horizon tragedy, represent a “poisoned chalice for an acquirer.”
“The deal looks dilutive to most of Shell’s key metrics, and we do not see the core strategic rationale for the combination,” Borkhataria added. “With Shell management having consistently communicated strategic priorities to the market since early 2023, the deal would also serve to contradict much of the commentary and potentially undermine credibility with its investor base. Shell would be much better served to continue with its plan and keep M&A smaller and more focused.”
This story was originally featured on Fortune.com